Role of estrogen and stress on the brain-gut axis American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology

El cerebro intestinal: emociones y digestión

The Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis
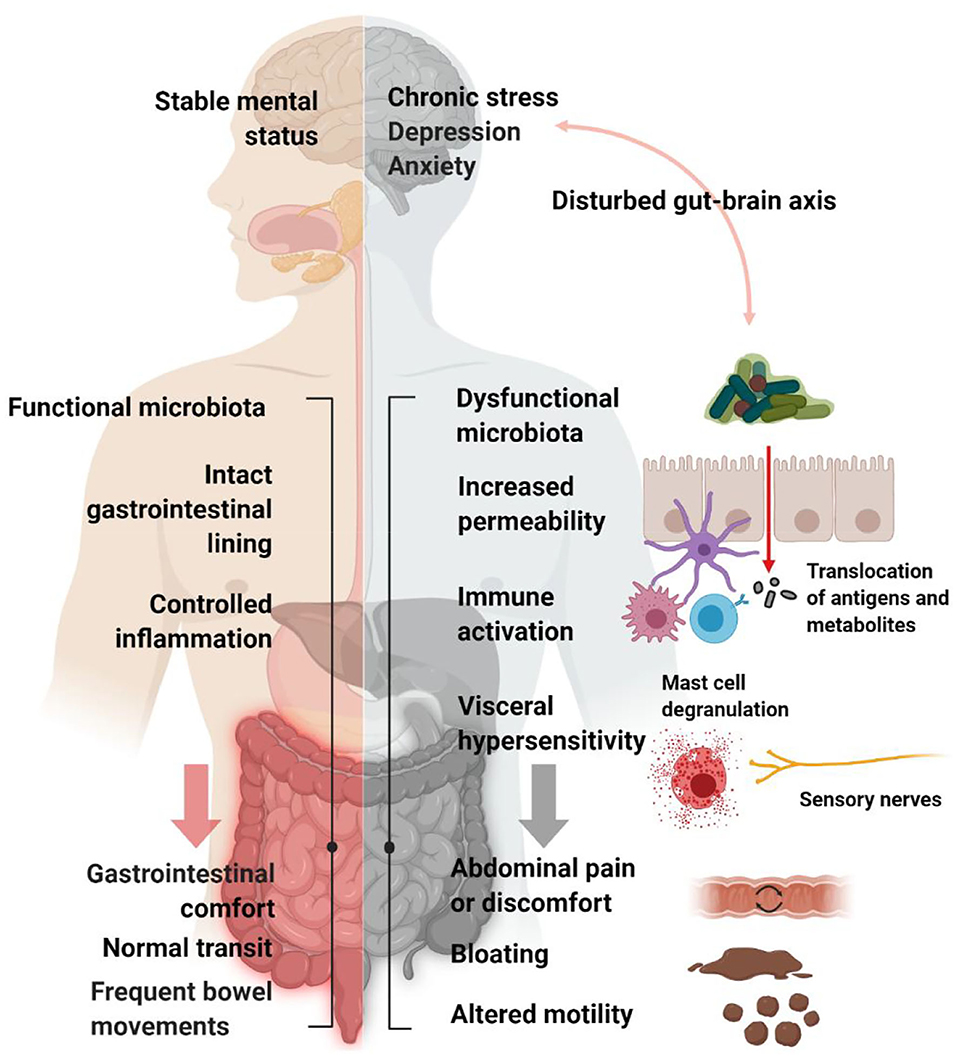
Frontiers Increasing Evidence That Irritable Bowel Syndrome and Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders Have a Microbial Pathogenesis
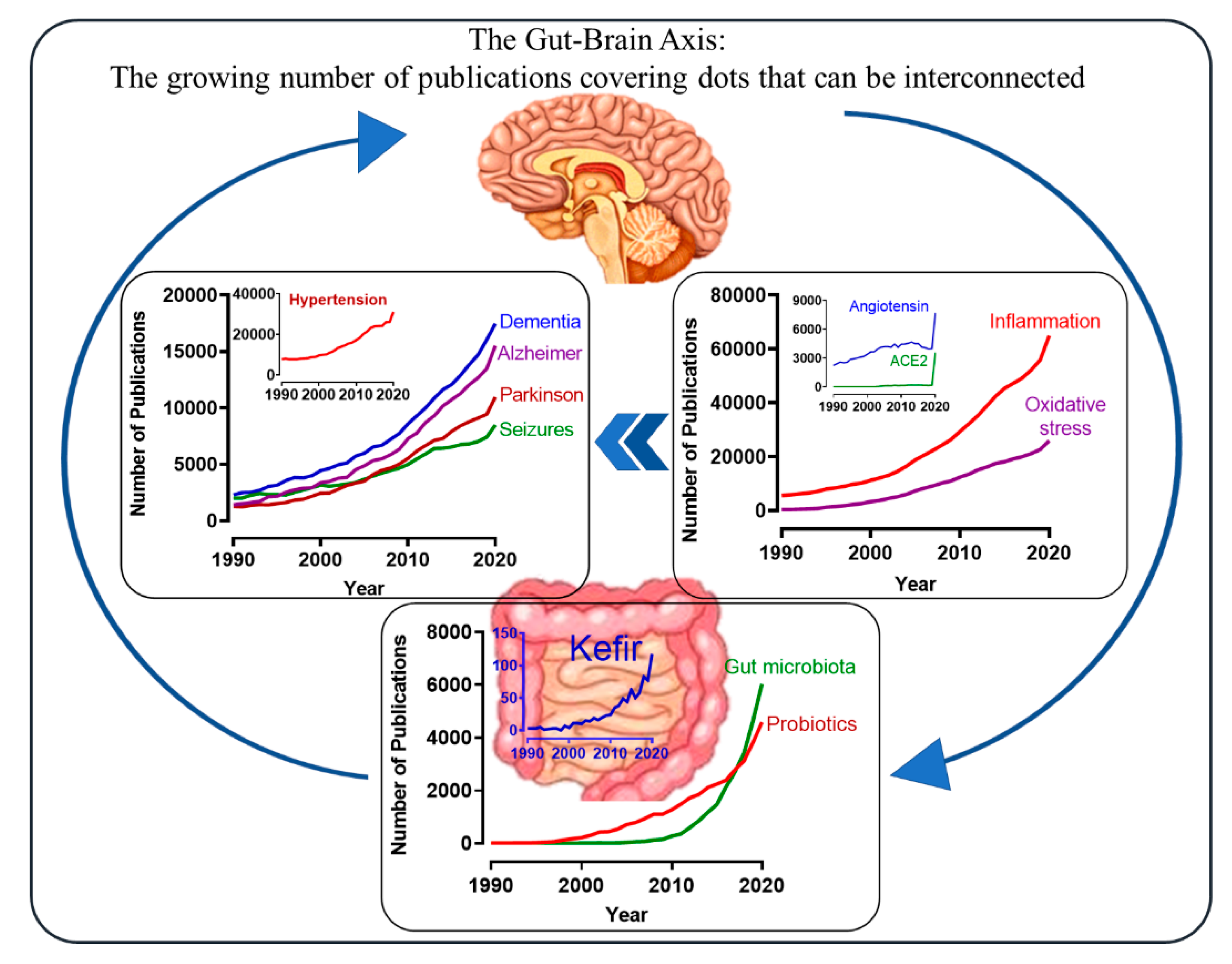
Antioxidants, Free Full-Text
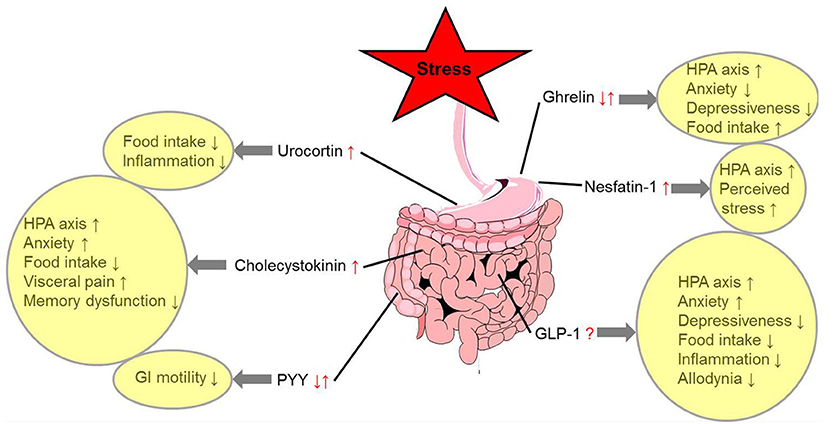
Frontiers Gut-Brain Neuroendocrine Signaling Under Conditions of Stress—Focus on Food Intake-Regulatory Mediators

American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology: Vol 317, No 4

Estrogen–gut microbiome axis: Physiological and clinical implications - ScienceDirect

G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 as a novel regulator of blood pressure

Brain-gut axis and sex hormones interaction in irritable bowel syndrome

Gut hormones and the regulation of energy homeostasis
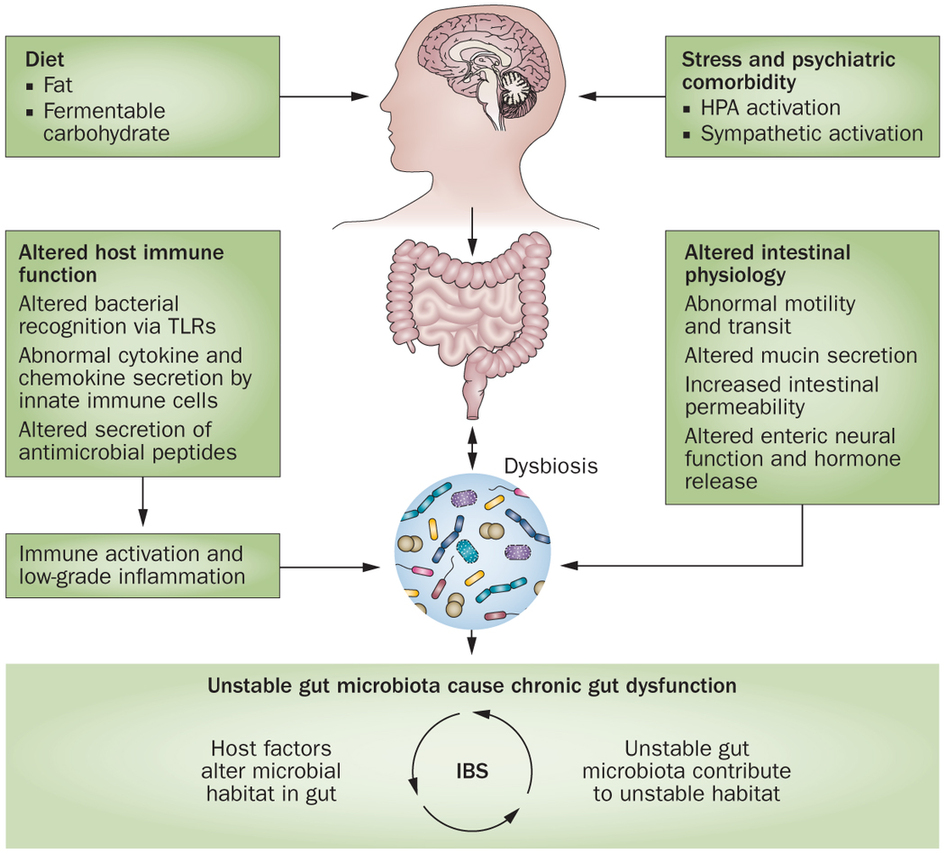
The Neuroendocrine System of the Gut and the Brain-Gut Axis (Gut-Brain Axis)
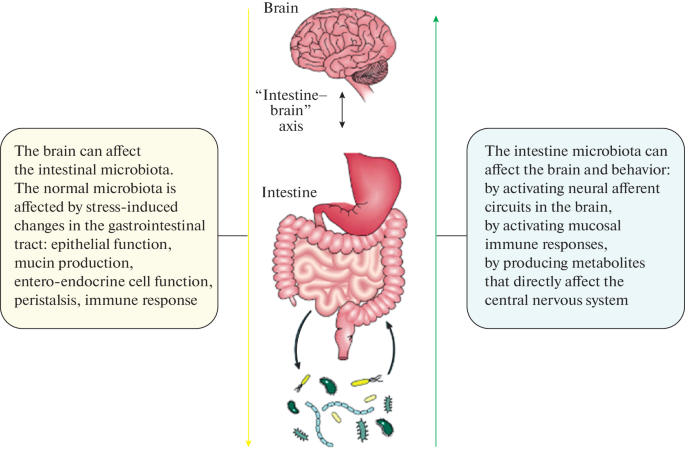
Causal Relationship between Physiological and Pathological Processes in the Brain and in the Gastrointestinal Tract: The Brain–Intestine Axis

The progress of gut microbiome research related to brain disorders, Journal of Neuroinflammation
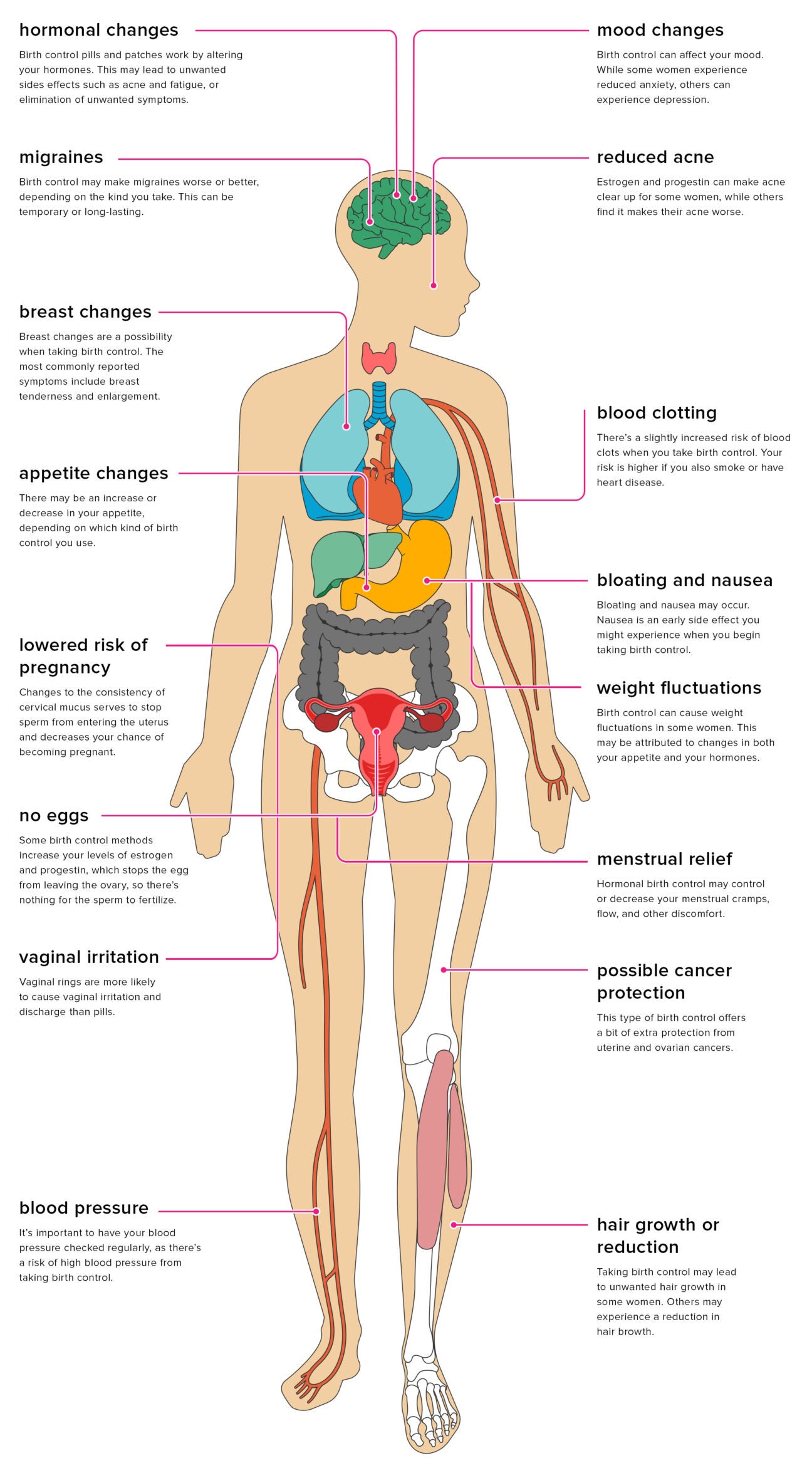


:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-is-a-menstrual-migraine-1719930-5c93bdb0c9e77c000149e4b1.png)





