Correlation between community participation, nutritional appetite and psychological distress among comorbid older persons, The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery
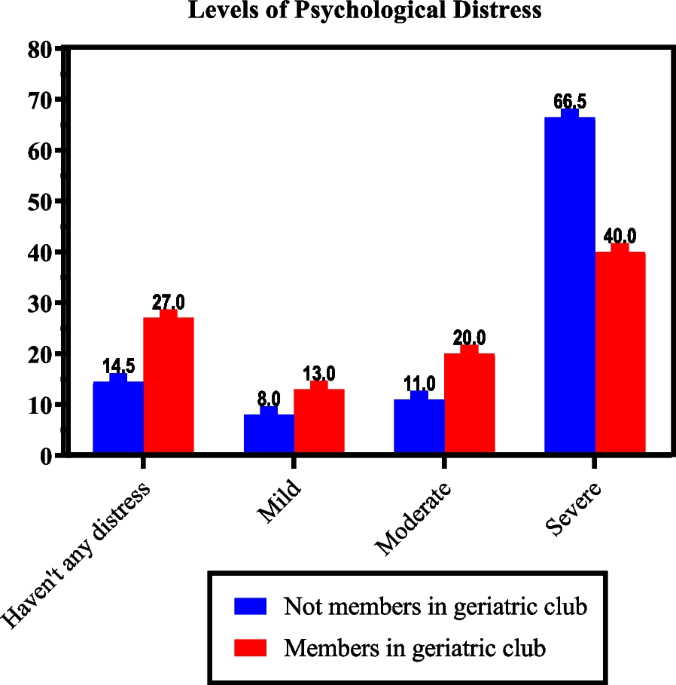
Background Poor appetite is a common problem among older people; it is known to contribute to weight loss, nutritional deficiencies, and increased mortality, which can affect their community participation and psychological status. In this study, we aimed to identify the relationship between community participation, nutritional appetite, and psychological distress among comorbid older people. This cross-sectional study included 300 elderly people, of whom 100 participated in geriatric clubs and 200 did not. Older people assessment sheet, the Australian Community Participation Questionnaire, the Council on Nutrition Appetite Questionnaire, and Kessler Psychological Distress Scale were used. Results Majority of geriatric club members had high community participation, while half of the older people who were not members of the club had moderate community participation levels. Approximately 41.0% of the participants at geriatric clubs had no risk at this time for a nutritional decline, while less than three-quarters of those who are not geriatric club members need frequent appetite reassessment. A correlation was observed between community participation with appetite and psychological distress in those who attended geriatric clubs. Those who are not geriatric club members had correlation between appetite with community participation and psychological distress (P ≤ 0.001). Conclusions Good appetite and psychological status are positively impacted by engaging in social activities among older people. Findings suggest that community programs, such as Meal on Wheels programs, and shared group activities can improve appetite and social interaction among older people.

The Relationship Between 5-Hydroxytryptamine and Its Metabolite Changes With Post-stroke Depression. - Abstract - Europe PMC

PDF) Prediction of Anger-in Based on Perceived Parenting & Early Maladaptive Schemas in Breast Cancer Patients
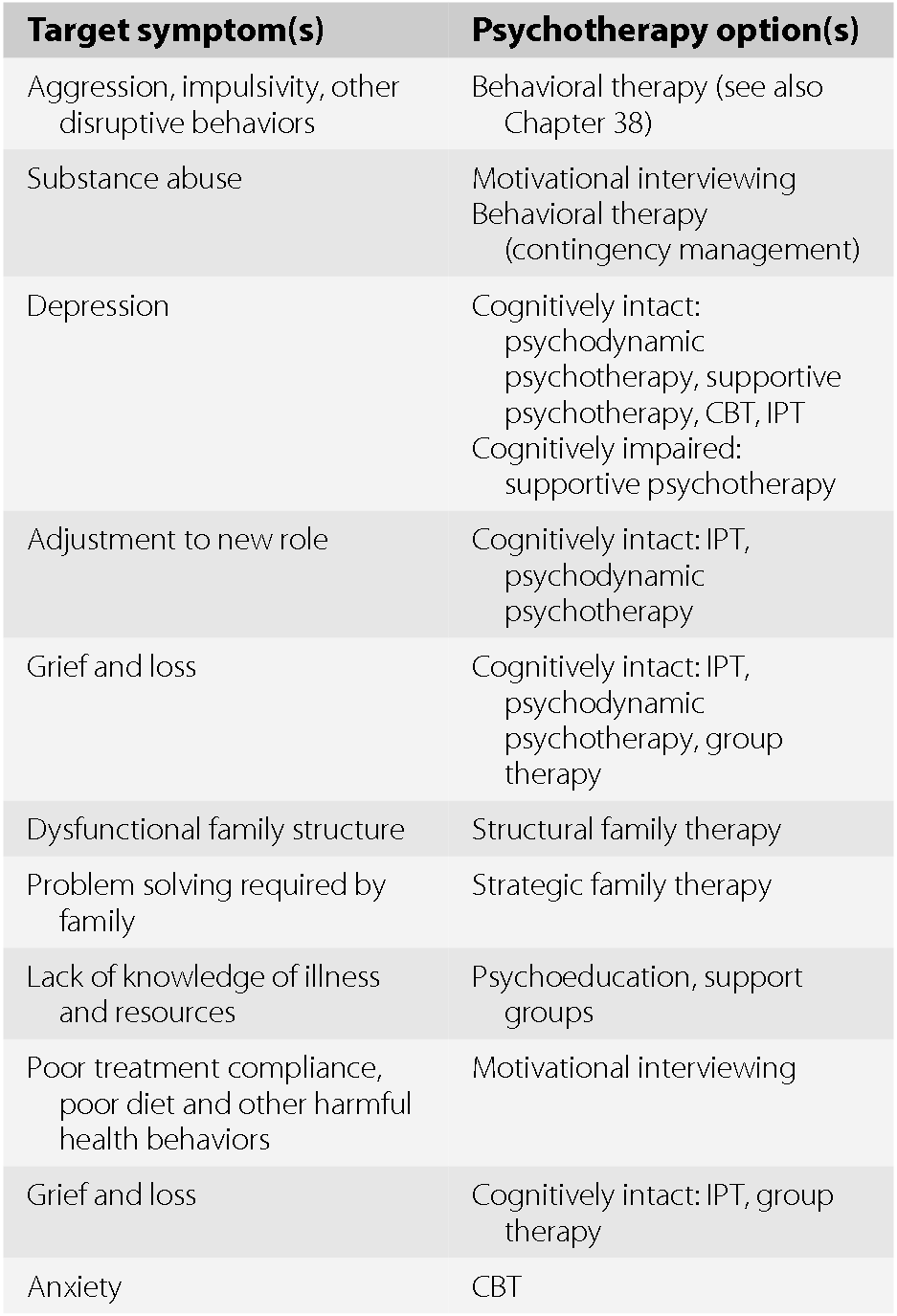
Treatments in Behavioral Neurology & Neuropsychiatry (Section III) - Behavioral Neurology & Neuropsychiatry

Prevalence and associated factors of depression among people with epilepsy in Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study, The Egyptian Journal of Neurology, Psychiatry and Neurosurgery

Full article: Does the presence of chronic pain affect scores on cognitive screening tests/brief cognitive measures for dementia? A systematic review and meta-analysis

Abstracts - 2014 - Asia-Pacific Journal of Clinical Oncology - Wiley Online Library

Abstracts - 2021 - Epilepsia - Wiley Online Library
IJERPH May 2018 - Browse Articles
Cancers July-1 2022 - Browse Articles

Role of diet and its effects on the gut microbiome in the pathophysiology of mental disorders

PDF) Psychological interventions for patients with rheumatic diseases and anxiety or depression
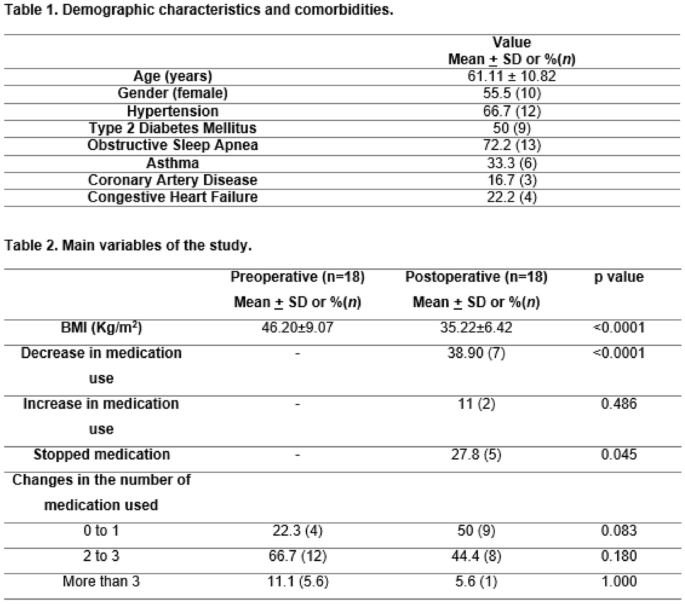
2021 Scientific Session of the Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES), Las Vegas, Nevada, 31 August–3 September 2021: Posters

Lowered oxygen saturation and increased body temperature in acute COVID-19 largely predict chronic fatigue syndrome and affective symptoms due to LONG COVID: a precision nomothetic approach