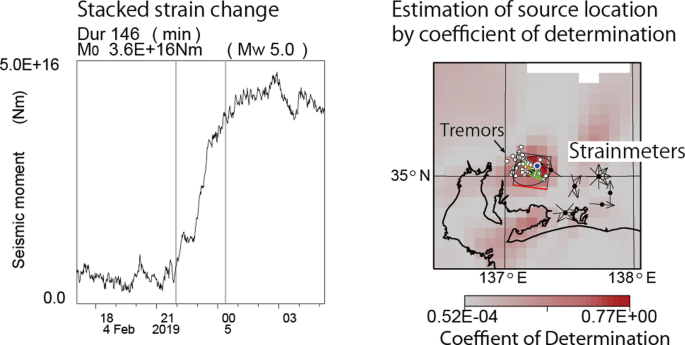
Temporary slip speed increases during short-term slow slip events with durations of one to three hours, Earth, Planets and Space
Temporary slip speed increases with durations of 1–3 h were identified during short-term slow slip events in records of borehole and laser strainmeters in the Tokai region, Japan. They were found by searching for peaks of correlation coefficients between stacked strain data and ramp functions with rise times of 1 and 2 h. Although many of the strain steps were considered due to noise, some strain steps occurred with simultaneous activation of the deep tectonic tremors and shared source areas with the tremors. From 2016 to 2022, we observed five strain steps with simultaneous activation of tectonic tremors and coincidence of source locations with the tremors. Those strain steps occurred during short-term slow slip events and were temporary slip speed increases of the slow slip events. Those strain steps seemed to be related to successive occurrences with source migration of short-term slow slip events. The detrended strain steps corresponded to plate boundary slip events of moment magnitude around 5, which was consistent with the scaling law of slow earthquakes. Graphical Abstract

Slow-slip, slow earthquakes, period-two cycles, full and partial ruptures, and deterministic chaos in a single asperity fault - ScienceDirect
An example of slow long-distance migration of LFEs during an ETS
2. The Rise of Earthquake Science, Living on an Active Earth: Perspectives on Earthquake Science

Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text

Source scaling relations and along‐strike segmentation of slow slip events in a 3‐D subduction fault model - Liu - 2014 - Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth - Wiley Online Library
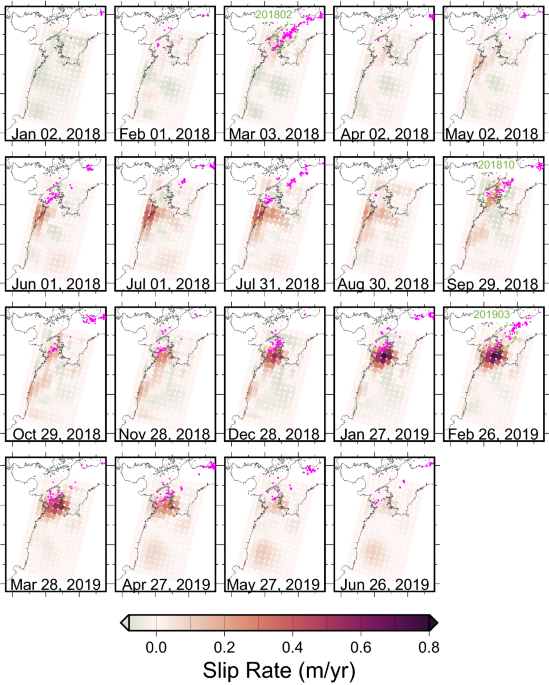
Long-term slow slip events with and without tremor activation in the Bungo Channel and Hyuganada, southwest Japan, Earth, Planets and Space

Mission Status
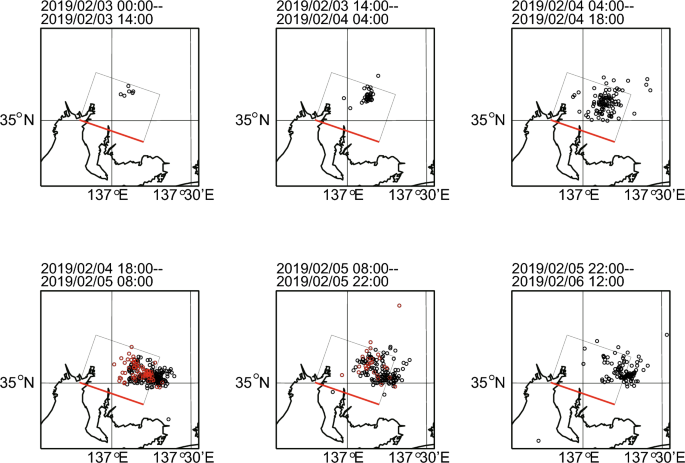
Temporary slip speed increases during short-term slow slip events with durations of one to three hours, Earth, Planets and Space

Effects of episodic slow slip on seismicity and stress near a subduction-zone megathrust
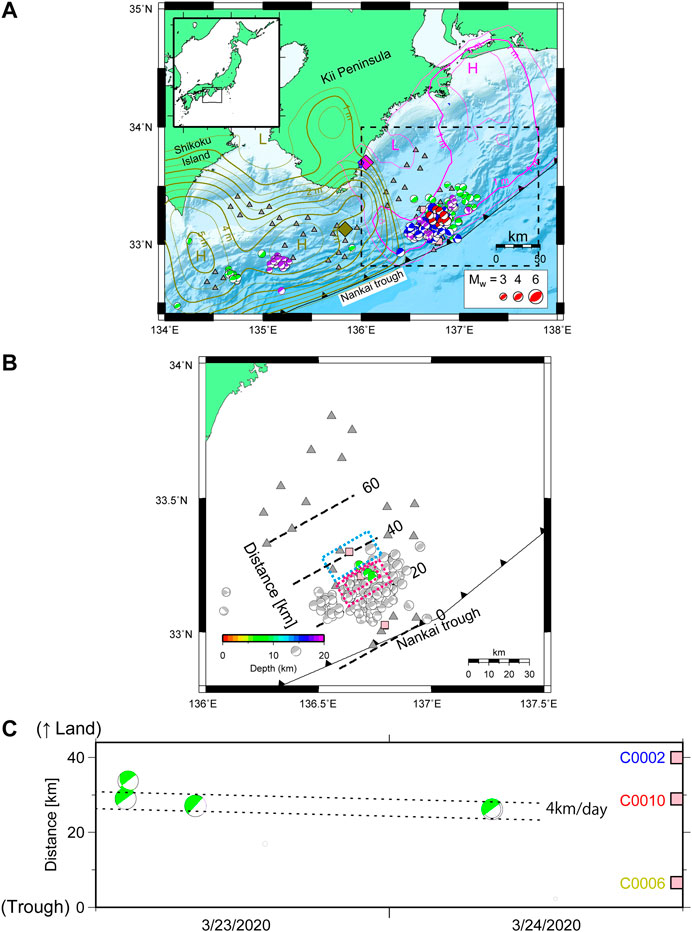
Frontiers Characteristics of Slow Slip Event in March 2020 Revealed From Borehole and DONET Observatories

PDF) Repeating short- and long-term slow slip events with deep tremor activity around the Bungo Channel region, southwest Japan

A Decade of Short‐Period Earthquake Rupture Histories From Multi‐Array Back‐Projection - Vera - 2024 - Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth - Wiley Online Library

The geophysics, geology and mechanics of slow fault slip - ScienceDirect
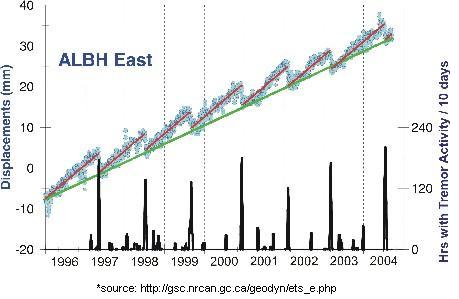
Pacific Northwest Tiltmeters









