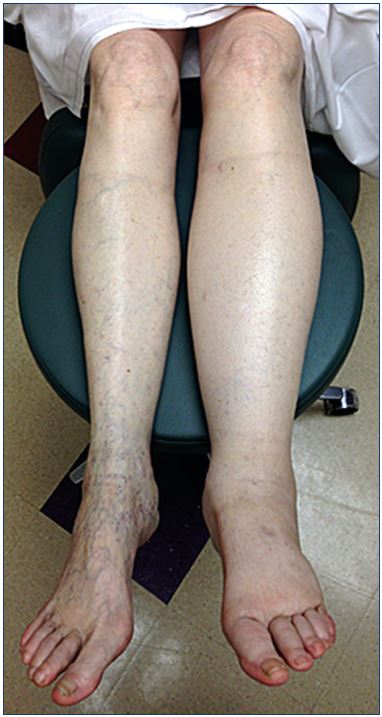
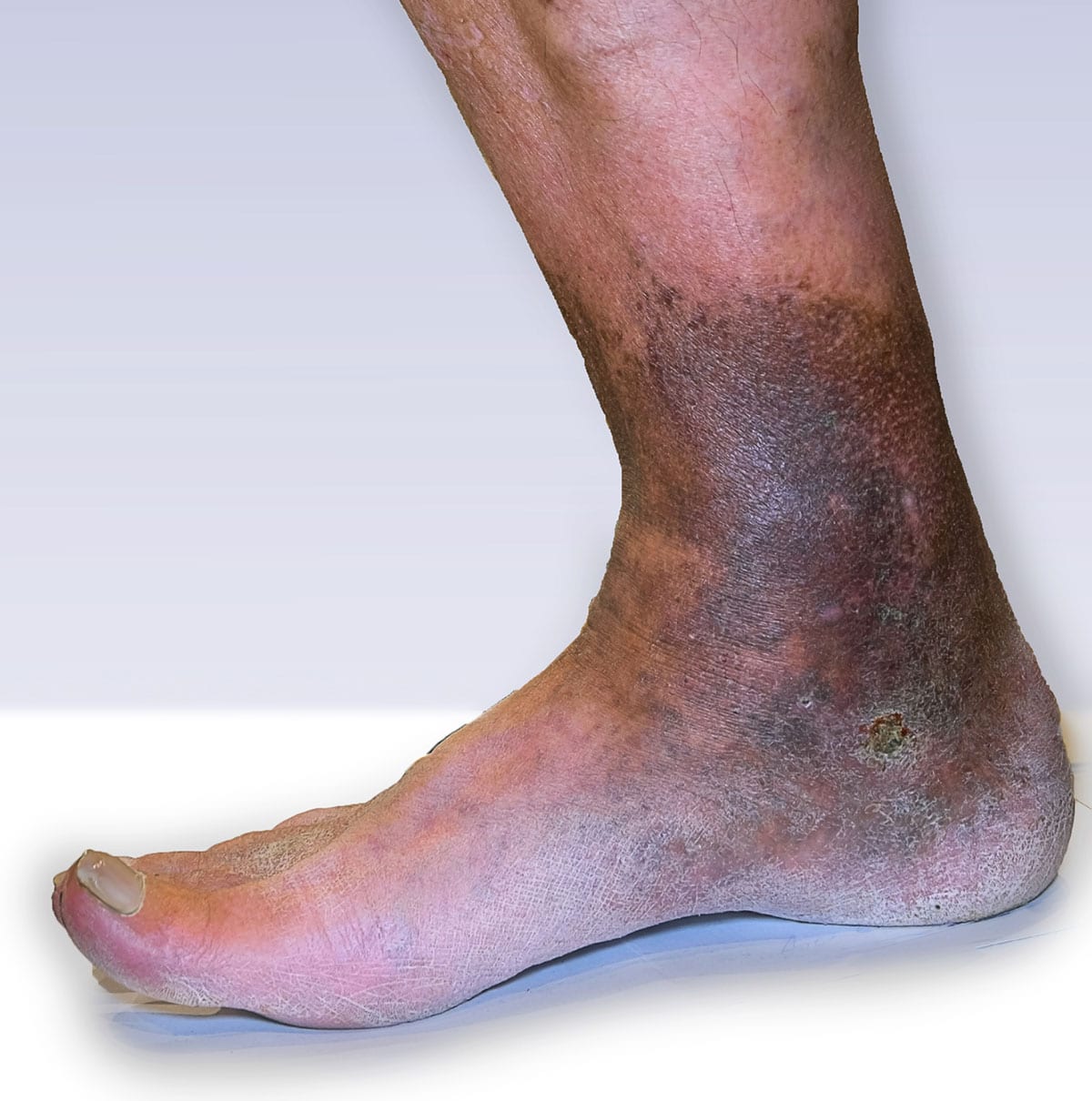
Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous
Mohamed K. KAMEL, John BLEBEA Department of Surgery, College of Medicine , Central Michigan University, Saginaw, MI, USA Abstract The prevalence of chronic venous insufficiency and its associated health care costs have been greatly underestimated for a long period of time. Many patients suffering from chronic venous insufficiency either present with or have associated lower-limb edema. The main pathophysiological mechanisms of edema formation in such patients include increased capillary hydrostatic pressures secondary to valvular insufficiency or venous obstruction. In addition, there is increased capillary permeability due to associated inflammatory reactions that subsequently lead to leakage of protein-rich fluid into the

Venous Insufficiency - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelf
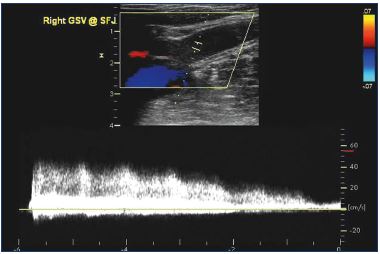
Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous
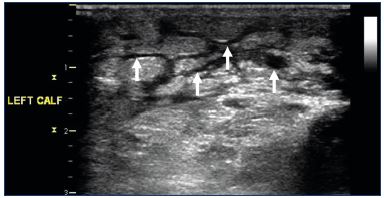
Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous

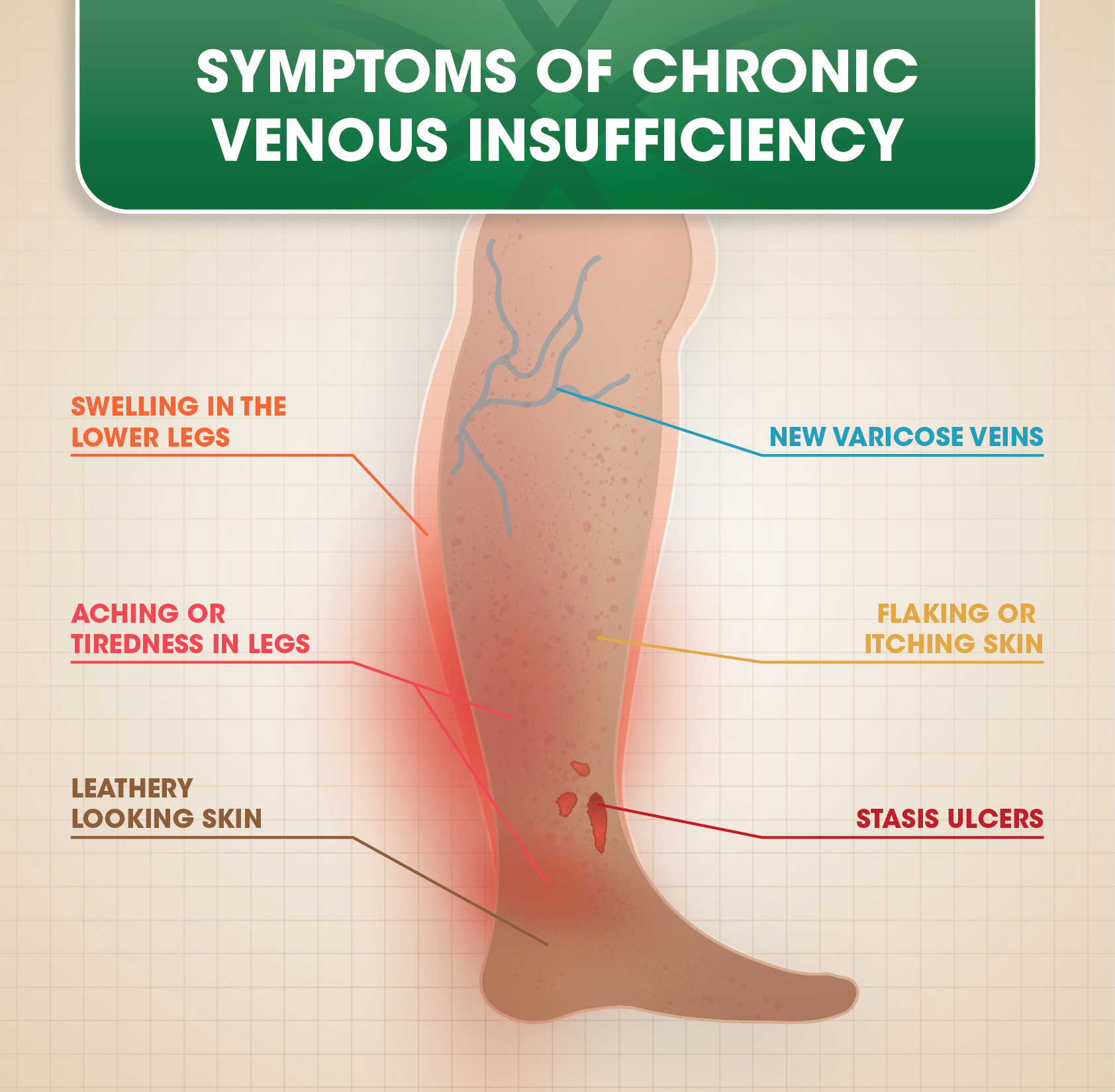
Venous hemodynamics and microcirculation in chronic venous

PDF] Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous
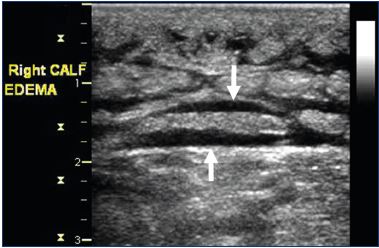
Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous

Endovenous laser ablation of the great and short saphenous veins
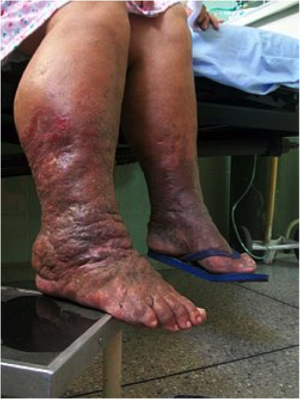
Peripheral Edema - Physiopedia
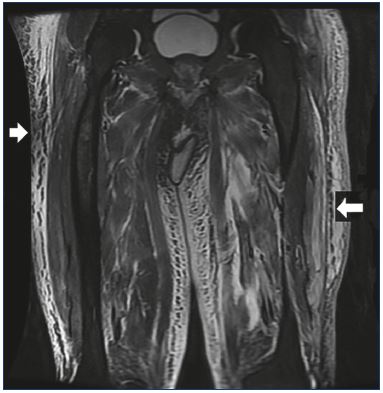
Pathophysiology of edema in patients with chronic venous

Quantitative measurement of pitting edema with a novel edema ruler

Peripheral Edema - Physiopedia

Peripheral Edema - Physiopedia
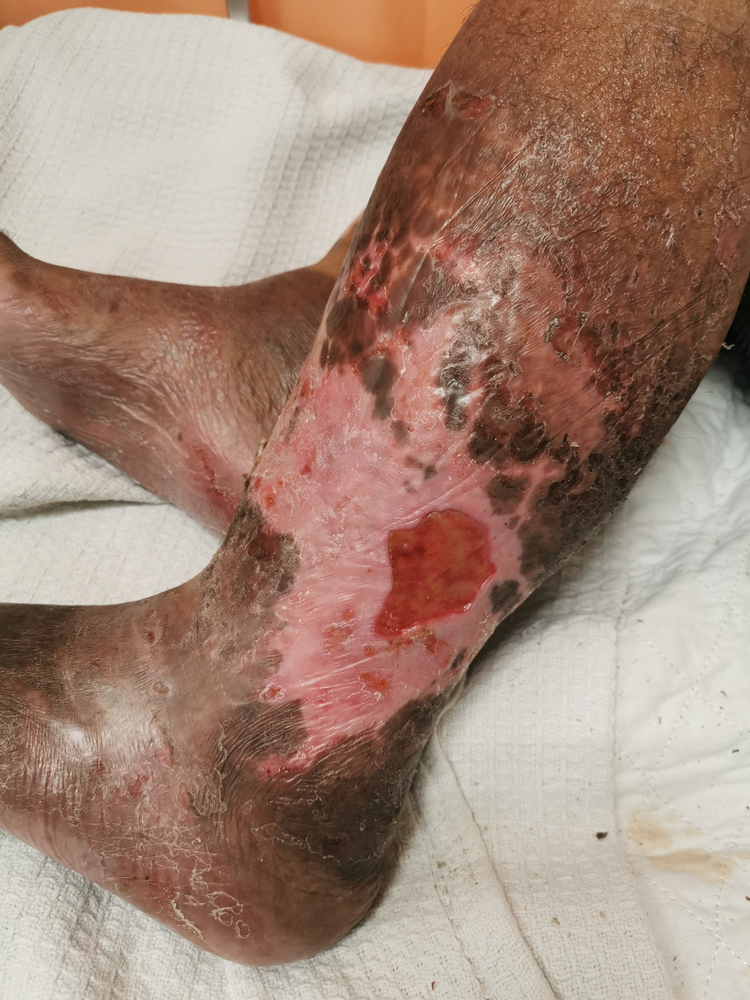


,aspect=fit)


