Forces directing germ-band extension in Drosophila embryos

Cellular, molecular, and biophysical control of epithelial cell intercalation. - Abstract - Europe PMC

A corset function of exoskeletal ECM promotes body elongation in Drosophila
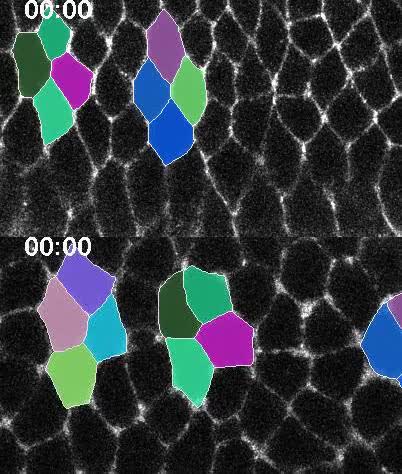
Src42A is required for E-cadherin dynamics at cell junctions during Drosophila axis elongation, Development

Cellular, molecular, and biophysical control of epithelial cell intercalation. - Abstract - Europe PMC

PDF) Forces directing germ-band extension in Drosophila embryos
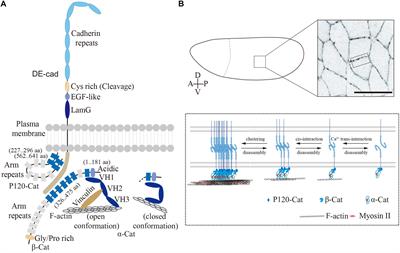
Frontiers Planar Cell Polarity and E-Cadherin in Tissue-Scale Shape Changes in Drosophila Embryos
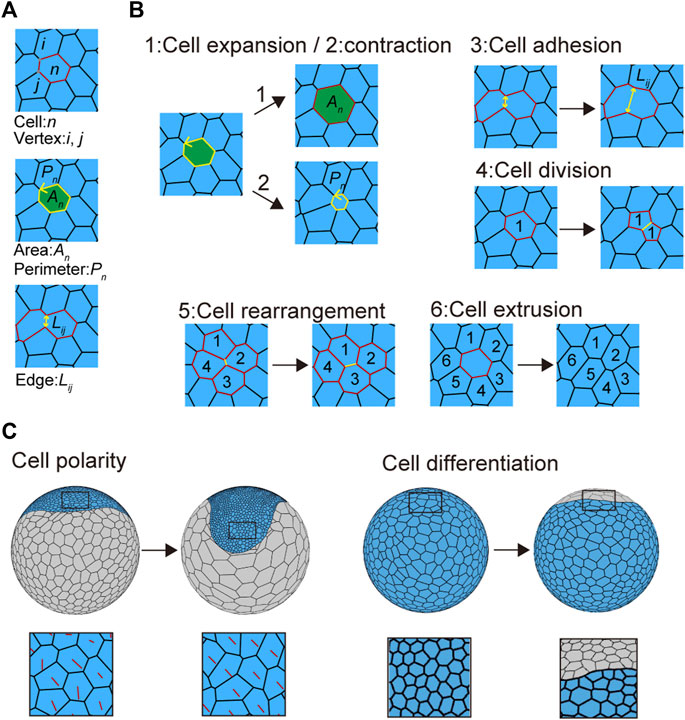
Frontiers Virtual spherical-shaped multicellular platform for simulating the morphogenetic processes of spider-like body axis formation
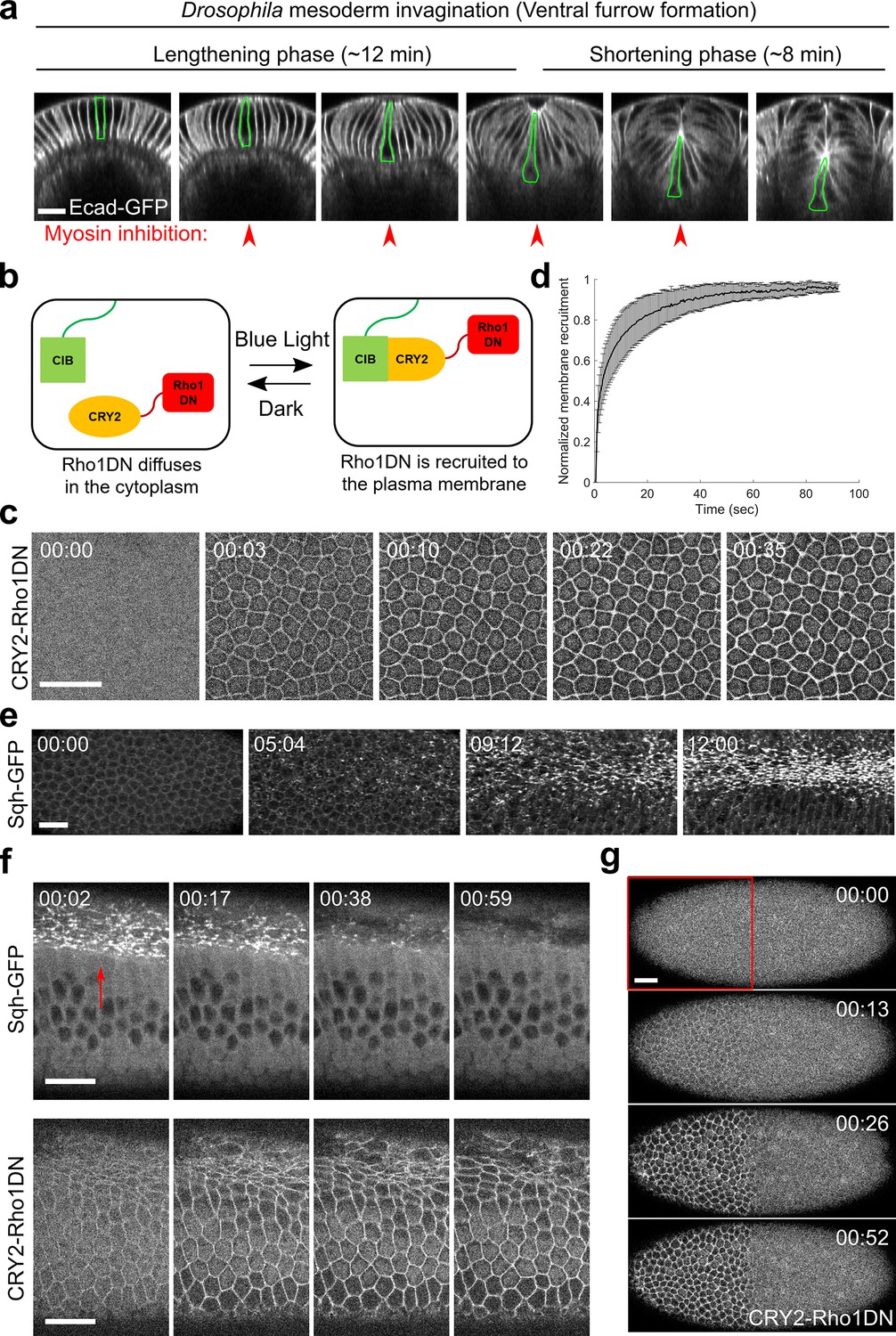
Optogenetic inhibition of actomyosin reveals mechanical bistability of the mesoderm epithelium during Drosophila mesoderm invagination

A corset function of exoskeletal ECM promotes body elongation in Drosophila
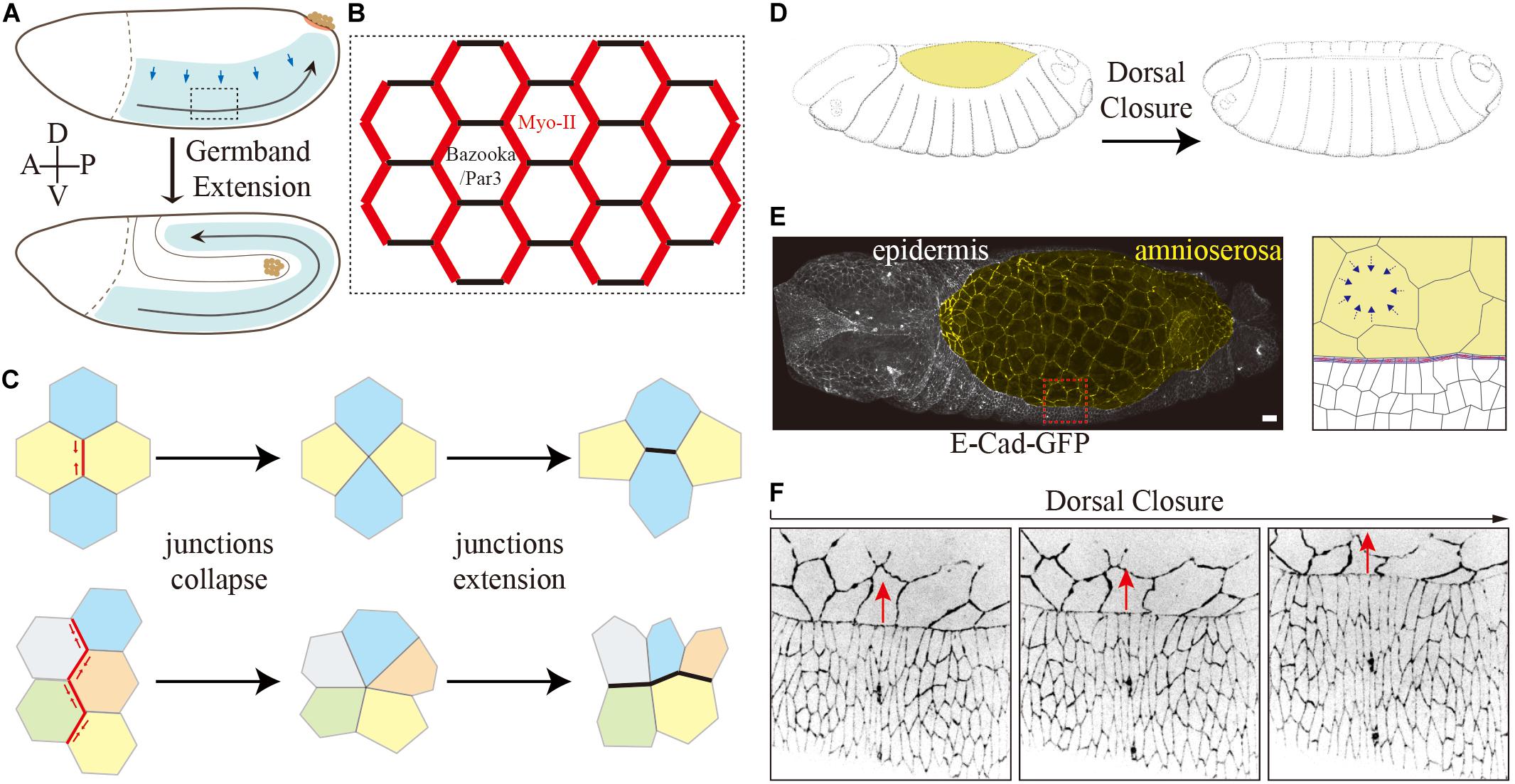
Frontiers Planar Cell Polarity and E-Cadherin in Tissue-Scale Shape Changes in Drosophila Embryos

Cellular, molecular, and biophysical control of epithelial cell intercalation. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Forces directing germ-band extension in Drosophila embryos - ScienceDirect









