The biorobotic demonstrator with Locusta migratoria individuals a
Download scientific diagram | The biorobotic demonstrator with Locusta migratoria individuals a. Different robotic stimuli to which L. migratoria was exposed are shown in b: gregarious-like biorobotic demonstrator (GL-BR), solitary-like biorobotic demonstrator (SL-BR), white biorobotic demonstrator (W-BR), gregarious-like neutral demonstrator (GL-N), solitary-like neutral demonstrator (SL-N), white neutral demonstrator (W-N) from publication: Robot-Locust Social Information Transfer Occurs in Predator Avoidance Contexts | Social learning is an evolutionarily important ability increasingly attributed also to invertebrate species. Interfacing robots with animals represents a promising strategy to investigate social learning. Herein, we studied if the gregarious form of Locusta migratoria, a | Social Informatics, Biomimetics and Predators | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Differences in identified neurons and neuronal circuits between

Israeli scientists develop sniffing robot with locust antennae

Locusta migratoria (migratory locust)

Design, Optimization, and Experiment on a Bioinspired Jumping

128698 PDFs Review articles in ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT

Robotic fly and a Ceratitis capitata adult male (a). The

20612 PDFs Review articles in GRASSHOPPERS

Green adults (a, b) and a brown adult (c) of L. migratoria

Sensorimotor control of navigation in arthropod and artificial

Mating success in Ceratitis capitata males that experienced or not

Sensorimotor control of navigation in arthropod and artificial

Locusta migratoria L., 1758, ssp. gallica Remaudière, 1947

128698 PDFs Review articles in ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT
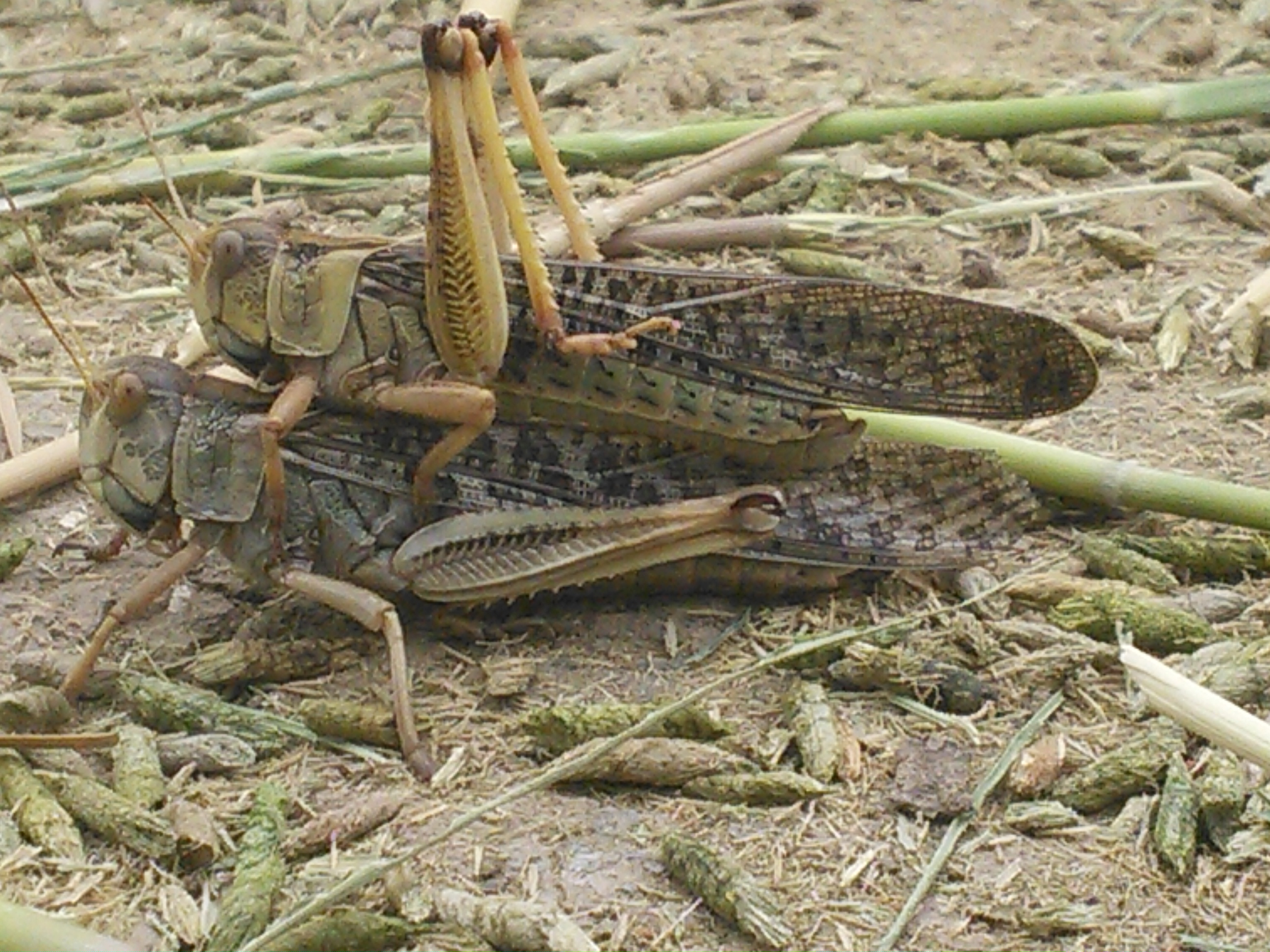

Plantwise Knowledge Bank

The desert locust's jumping behavior. (A) Side-view video