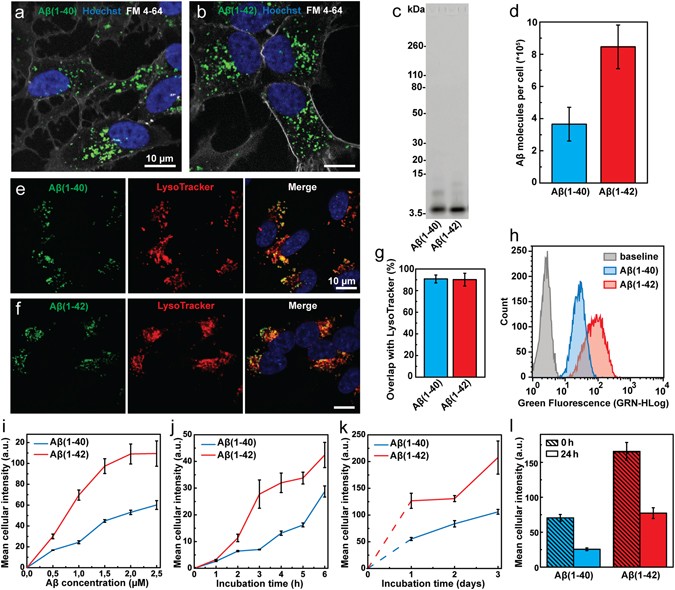
Endocytic uptake of monomeric amyloid-β peptides is clathrin- and dynamin-independent and results in selective accumulation of Aβ(1–42) compared to Aβ(1–40)

A delay in vesicle endocytosis by a C-terminal fragment of N-cadherin enhances Aβ synaptotoxicity
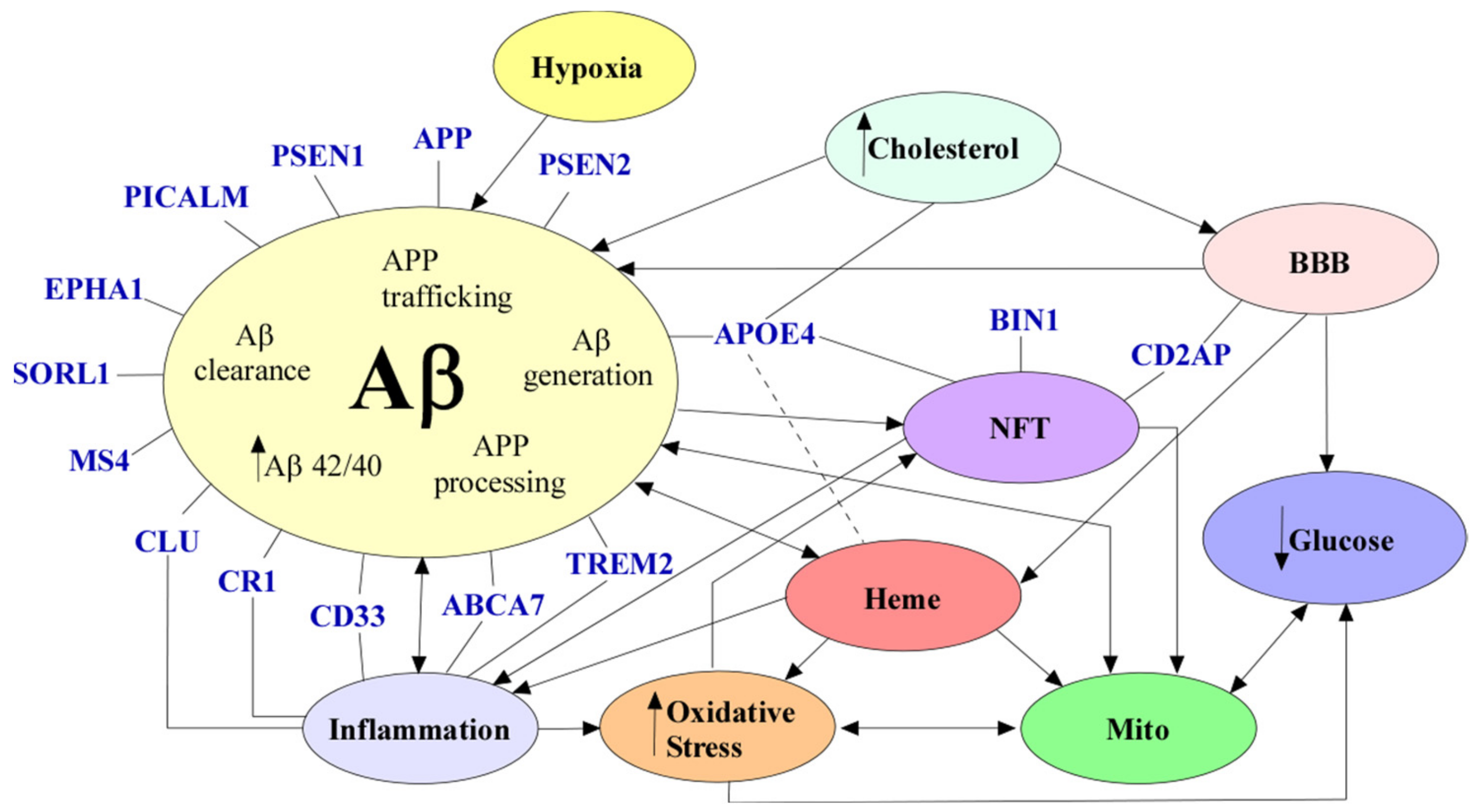
Cells, Free Full-Text

Misfolded amyloid-β-42 impairs the endosomal–lysosomal pathway
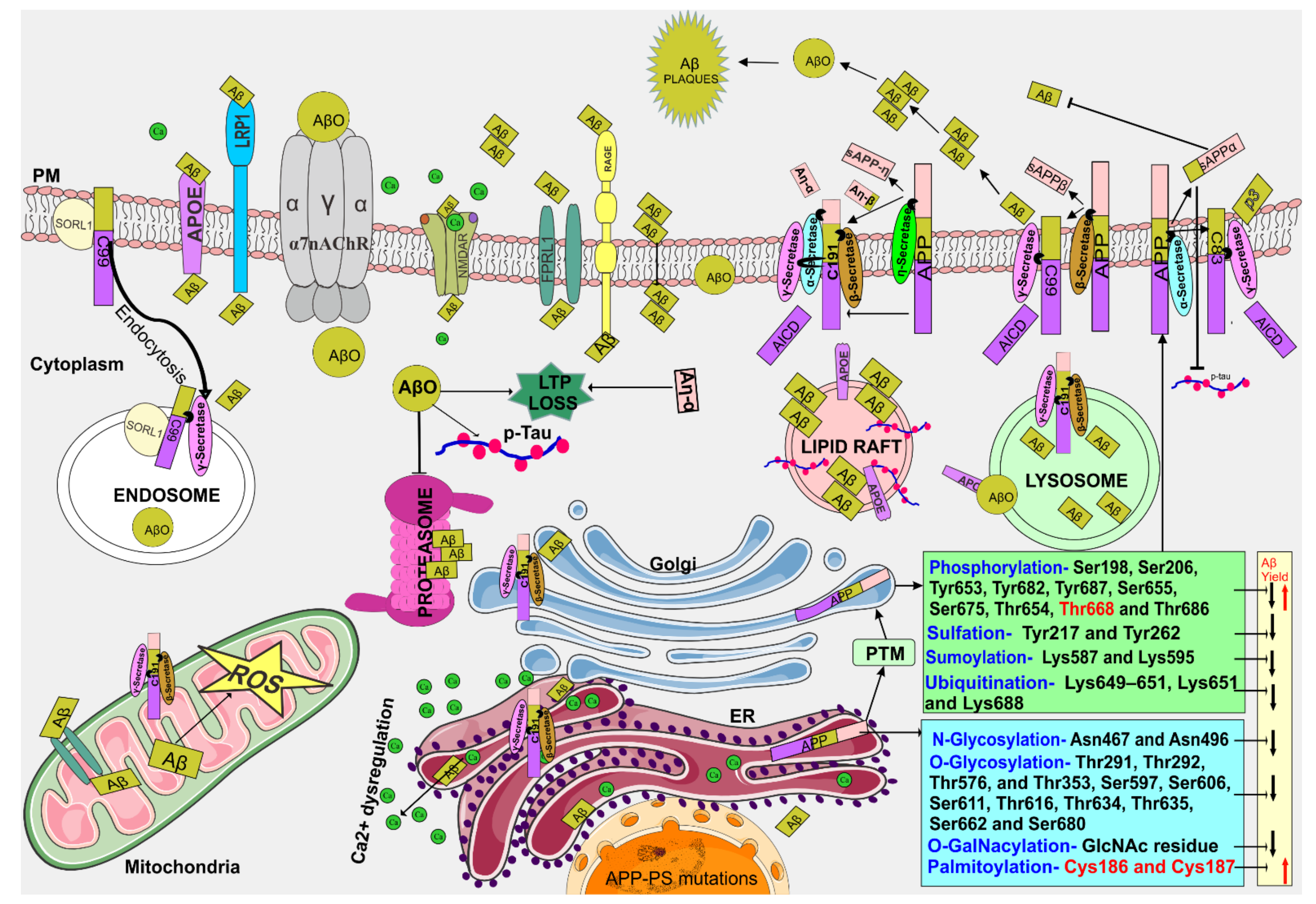
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

IJMS, Free Full-Text

In vivo synaptic activity-independent co-uptakes of amyloid β1–42 and Zn2+ into dentate granule cells in the normal brain
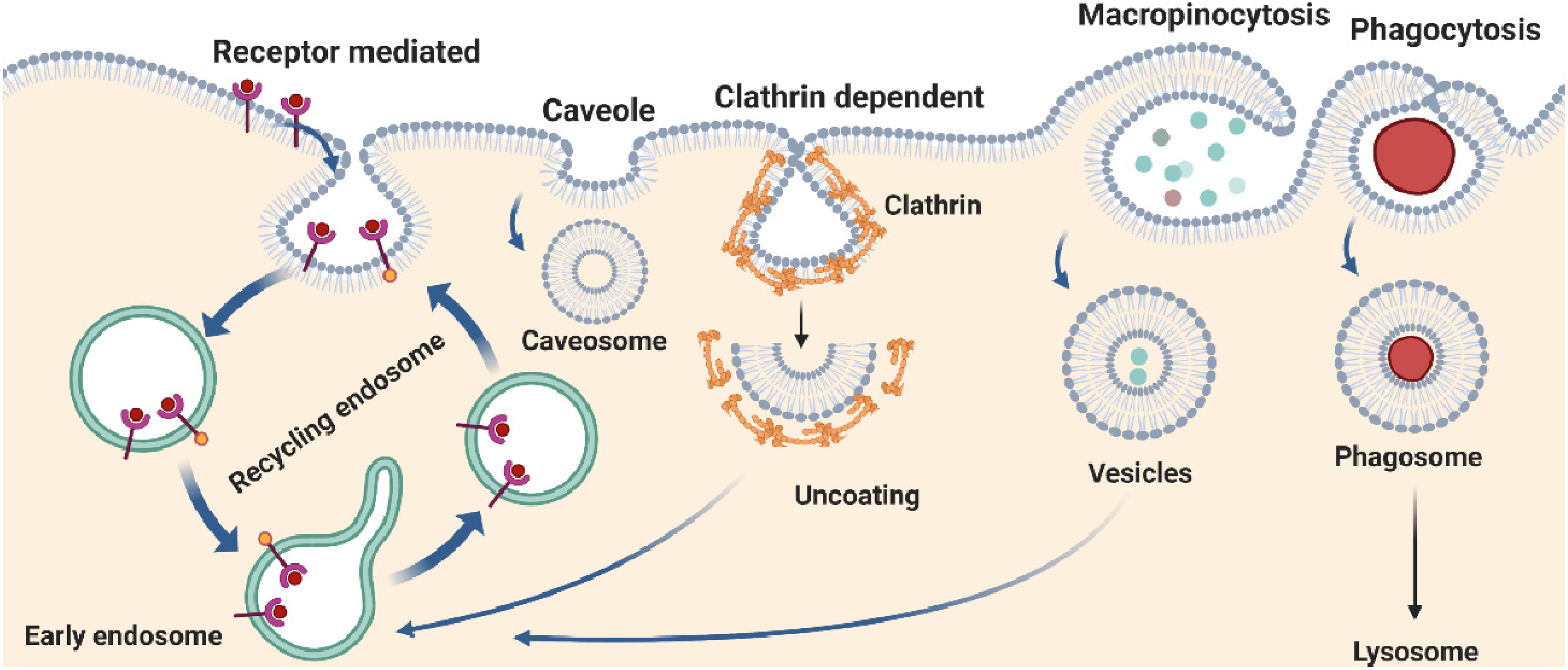
IJMS, Free Full-Text

Biomolecules, Free Full-Text

Alzheimer's disease linked Aβ42 exerts product feedback inhibition on γ-secretase impairing downstream cell signaling

Monomeric and Aggregated Tau Enter Neurons via Different Mechanisms (A)

IJMS, Free Full-Text

Uptake of Aβ by OATPs might be a new pathophysiological mechanism of Alzheimer disease, BMC Neuroscience

Designed Cell-Penetrating Peptide Inhibitors of Amyloid-beta Aggregation and Cytotoxicity - ScienceDirect

Mt3 deletion decreases Aβ endocytosis. a, b Confocal fluorescence









