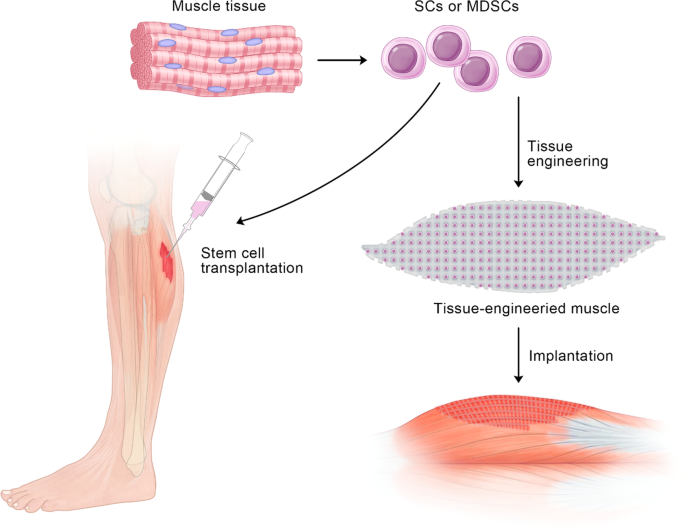
The role and therapeutic potential of stem cells in skeletal muscle in sarcopenia, Stem Cell Research & Therapy
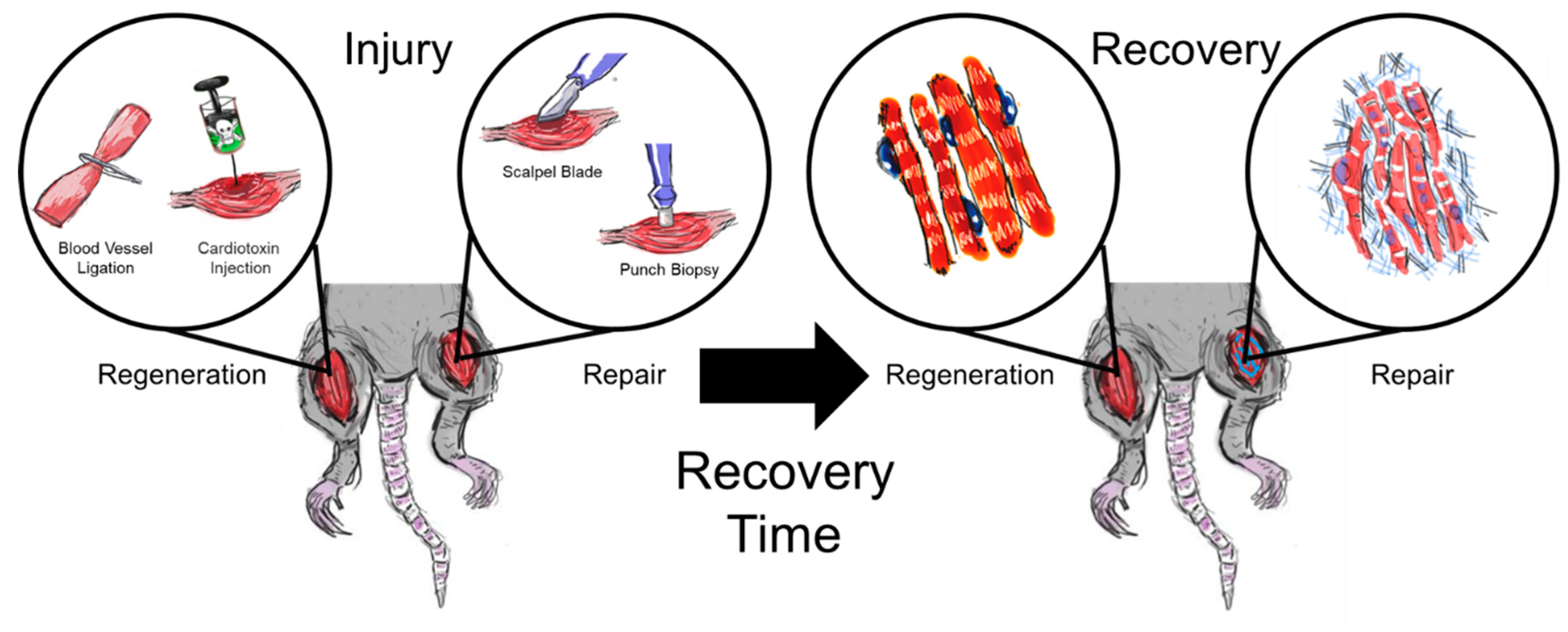
Sarcopenia is a common age-related skeletal muscle disorder featuring the loss of muscle mass and function. In regard to tissue repair in the human body, scientists always consider the use of stem cells. In skeletal muscle, satellite cells (SCs) are adult stem cells that maintain tissue homeostasis and repair damaged regions after injury to preserve skeletal muscle integrity. Muscle-derived stem cells (MDSCs) and SCs are the two most commonly studied stem cell populations from skeletal muscle. To date, considerable progress has been achieved in understanding the complex associations between stem cells in muscle and the occurrence and treatment of sarcopenia. In this review, we first give brief introductions to sarcopenia, SCs and MDSCs. Then, we attempt to untangle the differences and connections between these two types of stem cells and further elaborate on the interactions between sarcopenia and stem cells. Finally, our perspectives on the possible application of stem cells for the treatment of sarcopenia in future are presented. Several studies emerging in recent years have shown that changes in the number and function of stem cells can trigger sarcopenia, which in turn leads to adverse influences on stem cells because of the altered internal environment in muscle. A better understanding of the role of stem cells in muscle, especially SCs and MDSCs, in sarcopenia will facilitate the realization of novel therapy approaches based on stem cells to combat sarcopenia.

Mitochondrial dysfunction: roles in skeletal muscle atrophy, Journal of Translational Medicine
Metabolic reprogramming of skeletal muscle during aging and

Understanding the Therapeutic Potential of Bone Marrow Stem Cell Therapy in Ischemic Stroke
Nrf2 deficiency promotes the increasing trend of autophagy during aging in skeletal muscle: a potential mechanism for the development of sarcopenia

IBPS Stem Cells, Cardiovascular pathophysiology and Biothérapies

Skeletal muscle as potential central link between sarcopenia and immune senescence - ScienceDirect

Mitochondrial transplantation reduces lower limb ischemia-reperfusion injury by increasing skeletal muscle energy and adipocyte browning - ScienceDirect

Muscle‐secreted granulocyte colony‐stimulating factor functions as metabolic niche factor ameliorating loss of muscle stem cells in aged mice

Clinical-grade human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells improved skeletal muscle dysfunction in age-associated sarcopenia mice
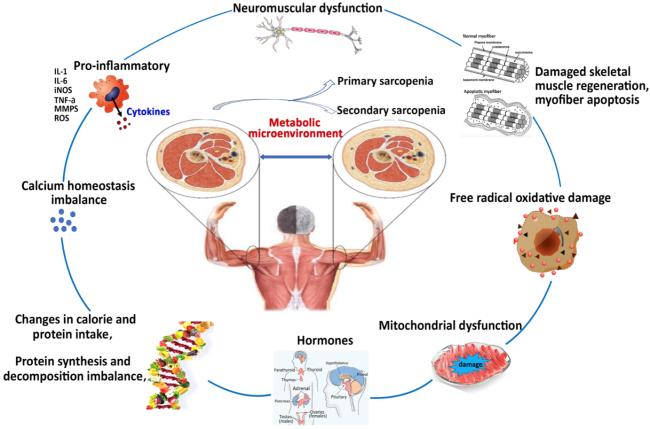
Skeletal Muscle Metabolic Alternation Develops Sarcopenia

Targeting Crosstalk of Signaling Pathways among Muscles-Bone-Adipose Tissue: A Promising Therapeutic Approach for Sarcopenia
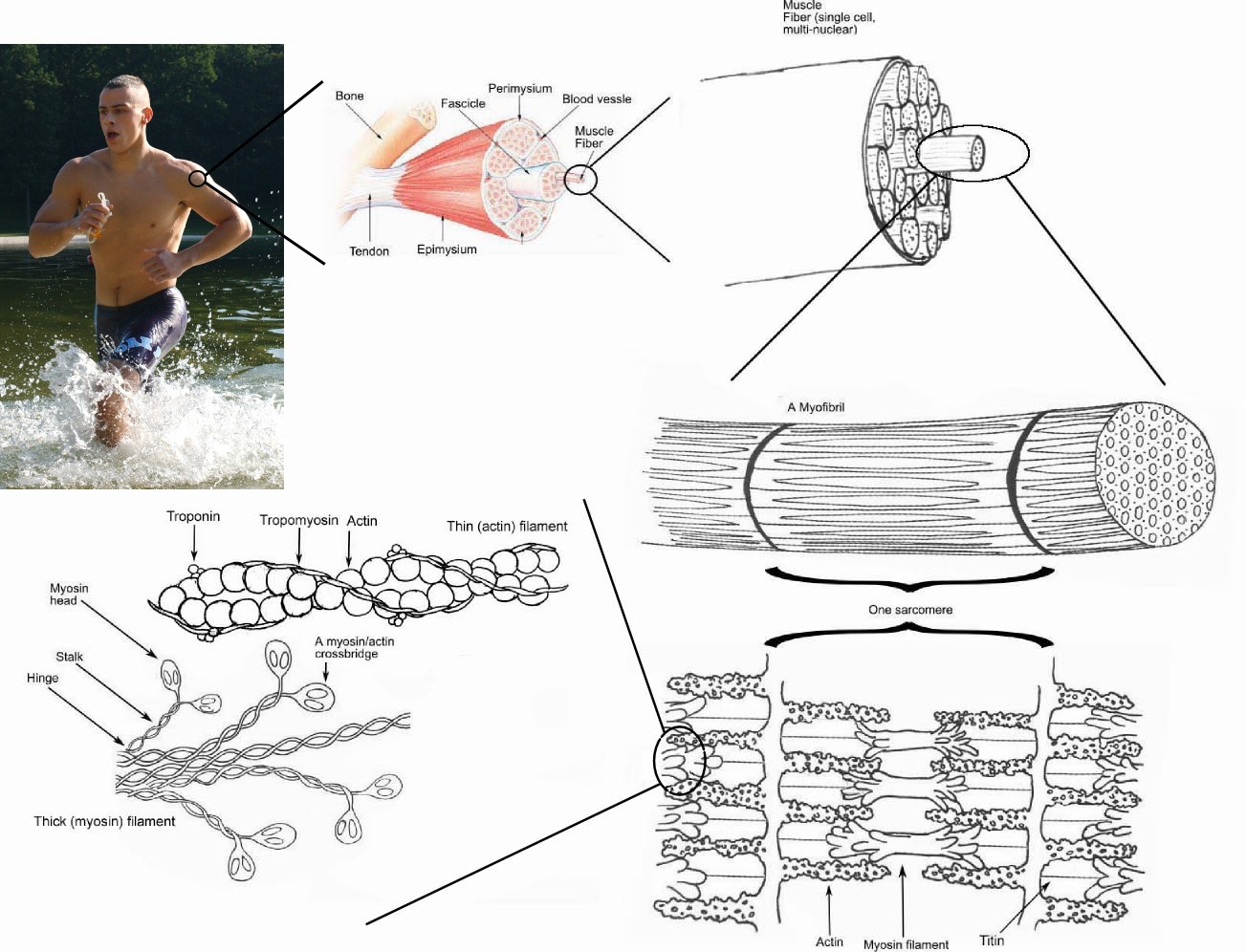
Skeletal muscle - Wikipedia

Stem cell-based therapies for musculoskeletal regeneration - The Physiological Society