The Rise and Fall of NGAL in Acute Kidney Injury
The nature and cellular sources of NGAL, its biological role and diagnostic ability in AKI and the increasing concerns surrounding its diagnostic and clinical value are described. For many years, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) has been considered the most promising biomarker of acute kidney injury (AKI). Commercial assays and point-of-care instruments, now available in many hospitals, allow rapid NGAL measurements intended to guide the clinician in the management of patients with or at risk of AKI. However, these assays likely measure a mixture of different NGAL forms originating from different tissues. Systemic inflammation, commonly seen in critically ill patients, and several comorbidities contribute to the release of NGAL from haematopoietic and non-haematopoietic cells. The unpredictable release and complex nature of the molecule and the inability to specifically measure NGAL released by tubular cells have hampered its use a specific marker of AKI in heterogeneous critically ill populations. In this review, we describe the nature and cellular sources of NGAL, its biological role and diagnostic ability in AKI and the increasing concerns surrounding its diagnostic and clinical value.

PDF) Serum NGAL, KIM-1, IL-18, L-FABP: new biomarkers in the
Biomarker Panel May Help Predict Kidney Damage in Patients With

Longitudinal NGAL and cystatin C plasma profiles present a high level of heterogeneity in a mixed ICU population, BMC Nephrology

Full article: Renal Restrictive Index (RRI) Versus Urinary

Neutrophil Gelatinase-assoc Lipocalin (NGAL): promising biomarker

Assessment of Cell-Cycle Arrest Biomarkers to Predict Early and Delayed Acute Kidney Injury

Impact of acute versus repetitive moderate intensity endurance exercise on kidney injury markers - Bongers - 2017 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library

Urine-based detection of biomarkers indicative of chronic kidney disease in a patient cohort from Ghana

PDF) Novel biomarkers of acute kidney injury and failure: Clinical applicability

Early Diagnostic and Prognostic Value of Urinary Neutrophil

Cystatin C and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin

PPT - Emerging Biomarkers of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) PowerPoint
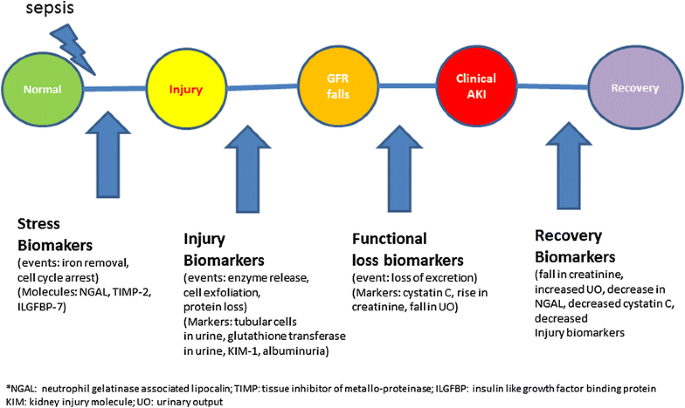
Acute kidney injury in sepsis
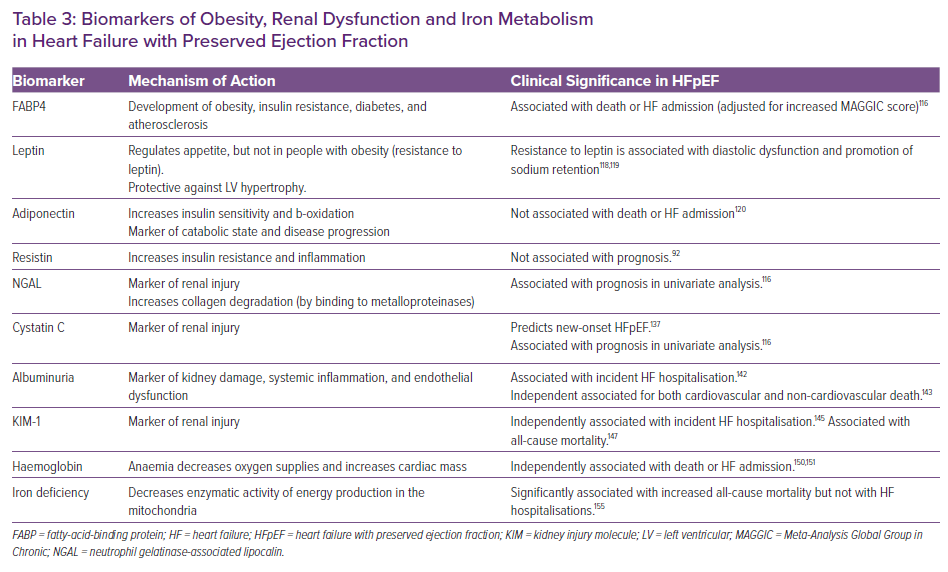
Biomarkers in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction