Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text
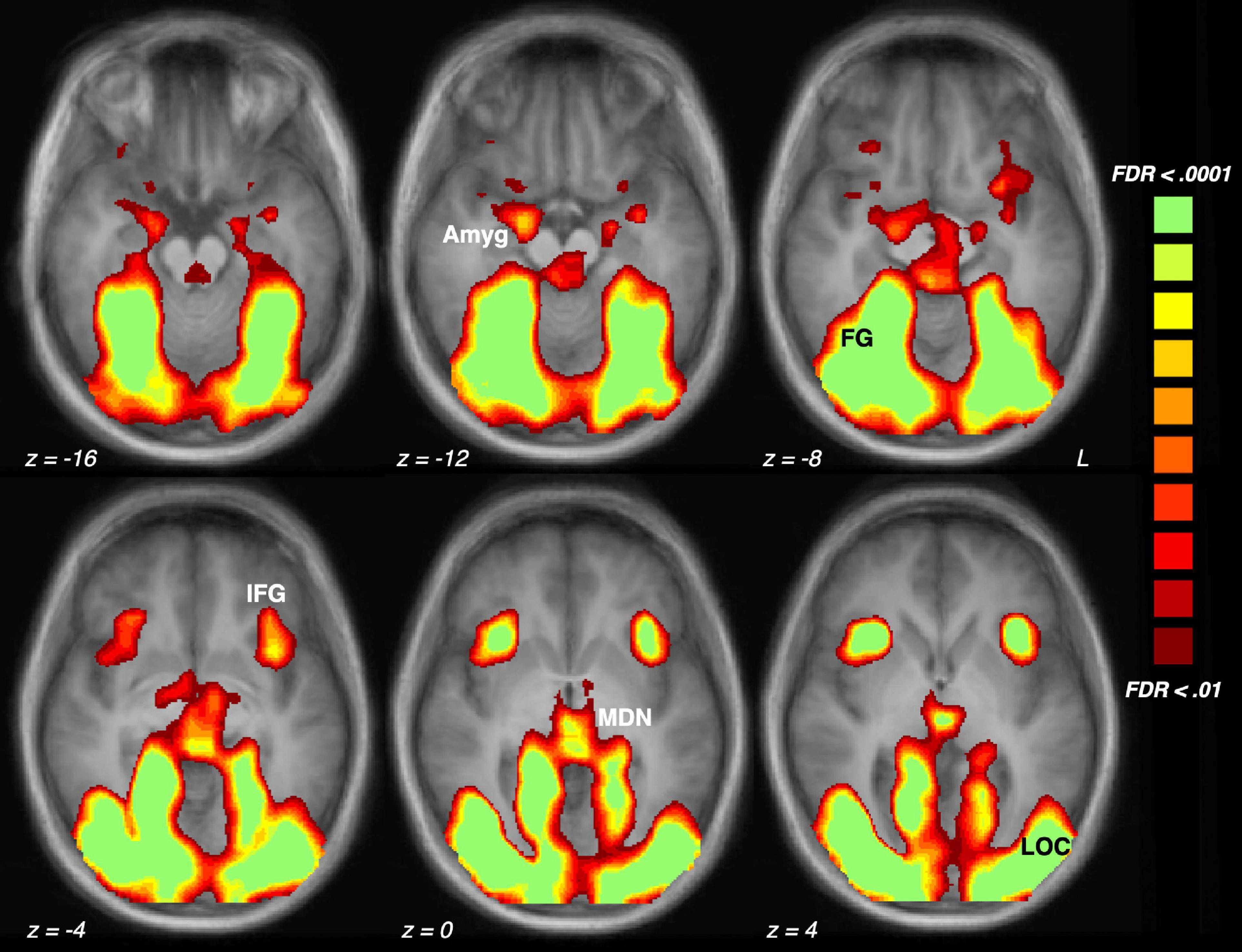
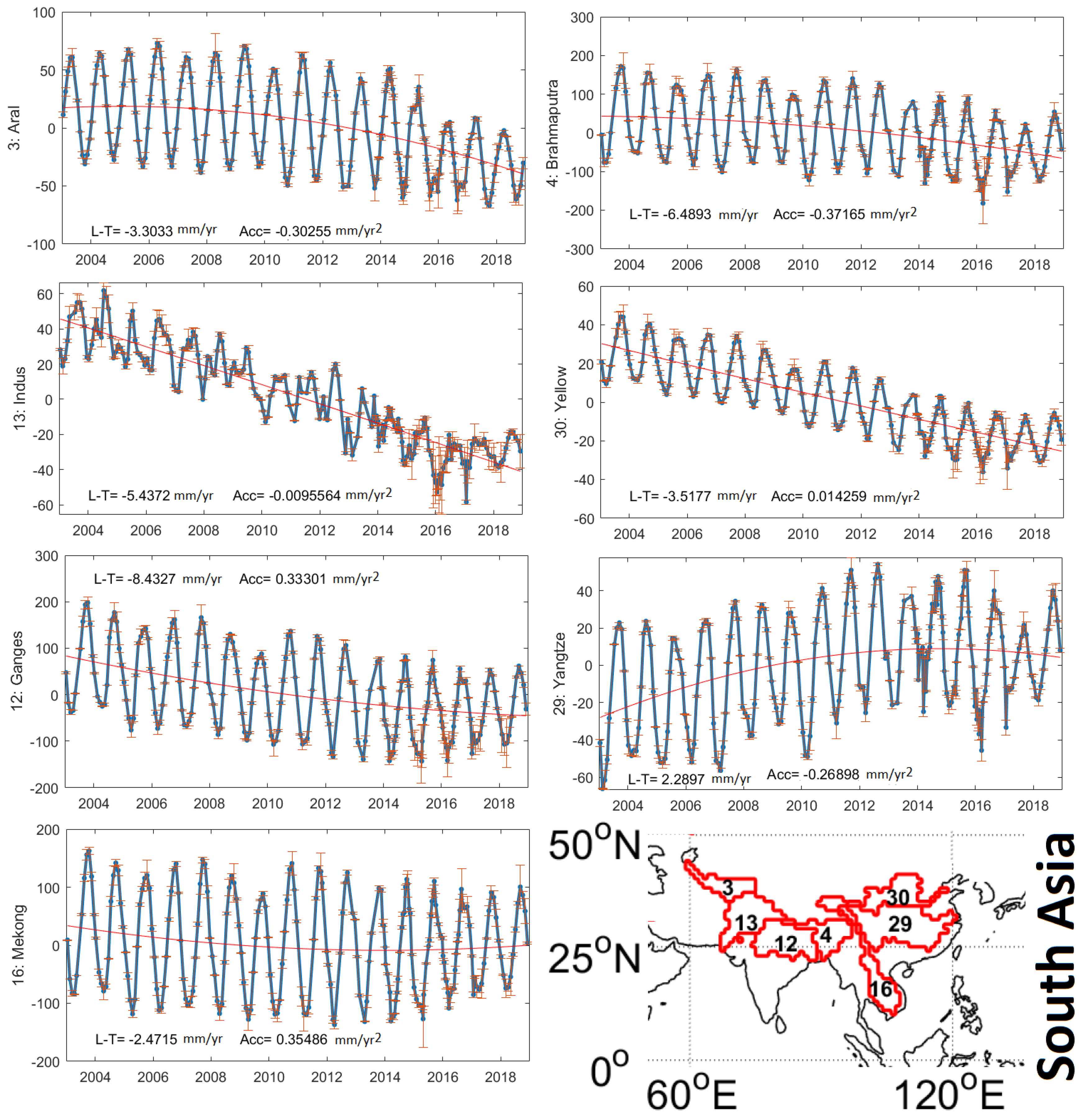
Observing global terrestrial water storage changes (TWSCs) from (inter-)seasonal to (multi-)decade time-scales is very important to understand the Earth as a system under natural and anthropogenic climate change. The primary goal of the Gravity Recovery And Climate Experiment (GRACE) satellite mission (2002–2017) and its follow-on mission (GRACE-FO, 2018–onward) is to provide time-variable gravity fields, which can be converted to TWSCs with ∼ 300 km spatial resolution; however, the one year data gap between GRACE and GRACE-FO represents a critical discontinuity, which cannot be replaced by alternative data or model with the same quality. To fill this gap, we applied time-variable gravity fields (2013–onward) from the Swarm Earth explorer mission with low spatial resolution of ∼ 1500 km. A novel iterative reconstruction approach was formulated based on the independent component analysis (ICA) that combines the GRACE and Swarm fields. The reconstructed TWSC fields of 2003–2018 were compared with a commonly applied reconstruction technique and GRACE-FO TWSC fields, whose results indicate a considerable noise reduction and long-term consistency improvement of the iterative ICA reconstruction technique. They were applied to evaluate trends and seasonal mass changes (of 2003–2018) within the world’s 33 largest river basins.

Tribology in renewable energy - About Tribology

Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation by Thomas M. Lillesand

Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text, está bogaz 0.41

FREE Access to the Leading GIS & Remote Sensing Journals - GIS
Flowchart Of Remote Sensing Data Extraction Source Author S

ARSET - Satellite Remote Sensing for Agricultural Applications

Cloud and snow detection of remote sensing images based on improved Unet3+

Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text

Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text, scp 7141
Remote Sensing, Free Full-Text, scp 7141