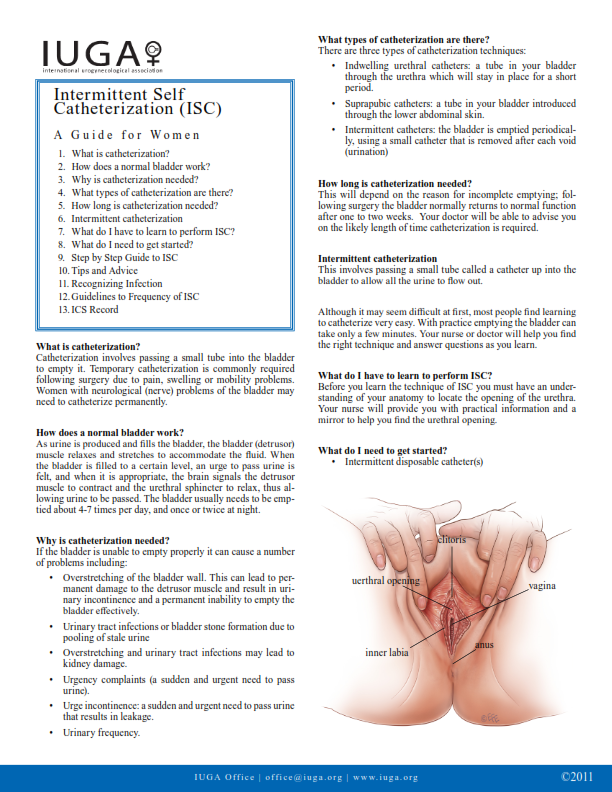
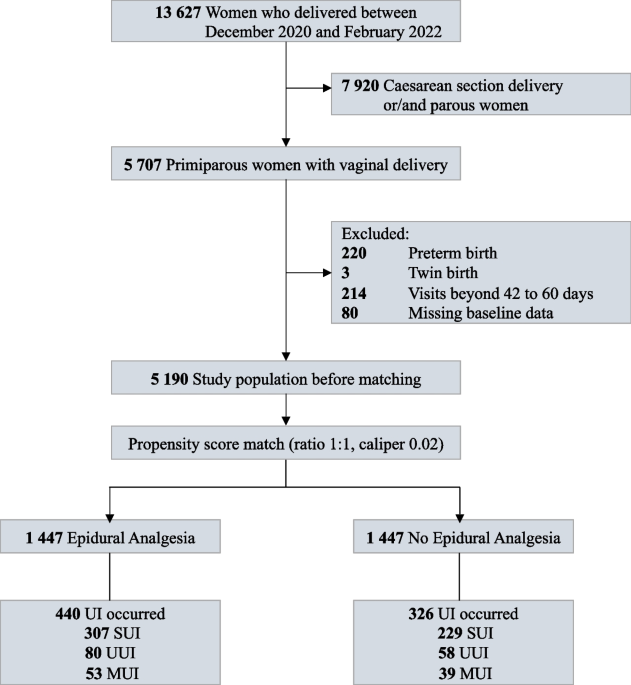
Assessment of Obstetric Risk Factors for Postpartum Urinary Retention After Vaginal Delivery: A Case-Control Study, PDF, Childbirth
Jurnal - Postpartum Urinary Retention - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt / .pptx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This study assessed risk factors for postpartum urinary retention (PPUR) after vaginal delivery in 234 women. PPUR was defined as a postvoid residual bladder volume ≥150 mL or inability to void within 6 hours of delivery. 19 women (8.1%) developed PPUR. Logistic regression found prolonged second stage of labor, episiotomy, perineal laceration, and birth weight >4000g were independent risk factors for PPUR. The study aims to identify women at risk to prevent PPUR and complications.
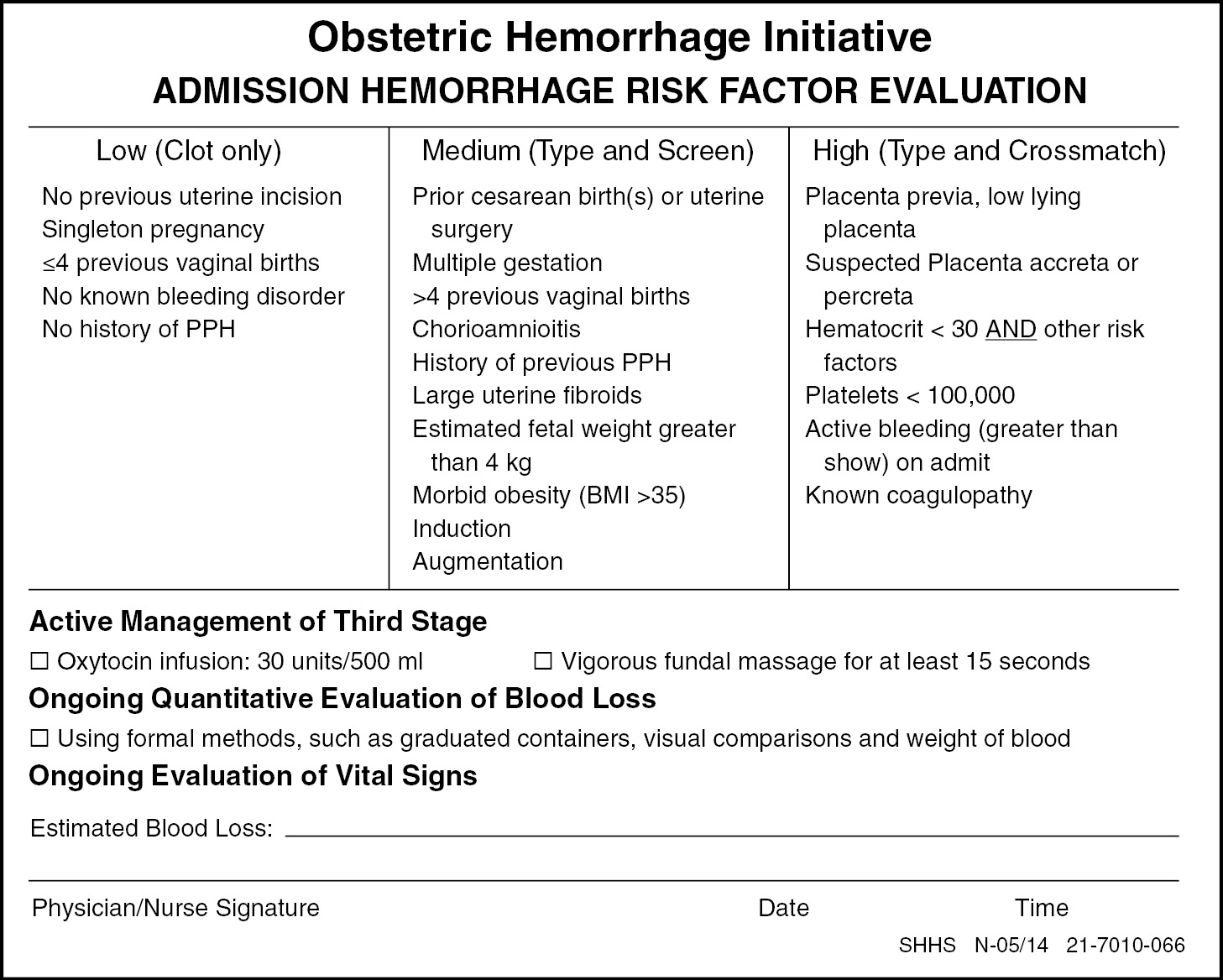
Postpartum Hemorrhage (Chapter 28) - Obstetric Care

The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after vaginal

SciELO - Brasil - Risk factors for postpartum urinary incontinence

PDF) The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after

Chapter 5: Postpartum Care

The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after vaginal
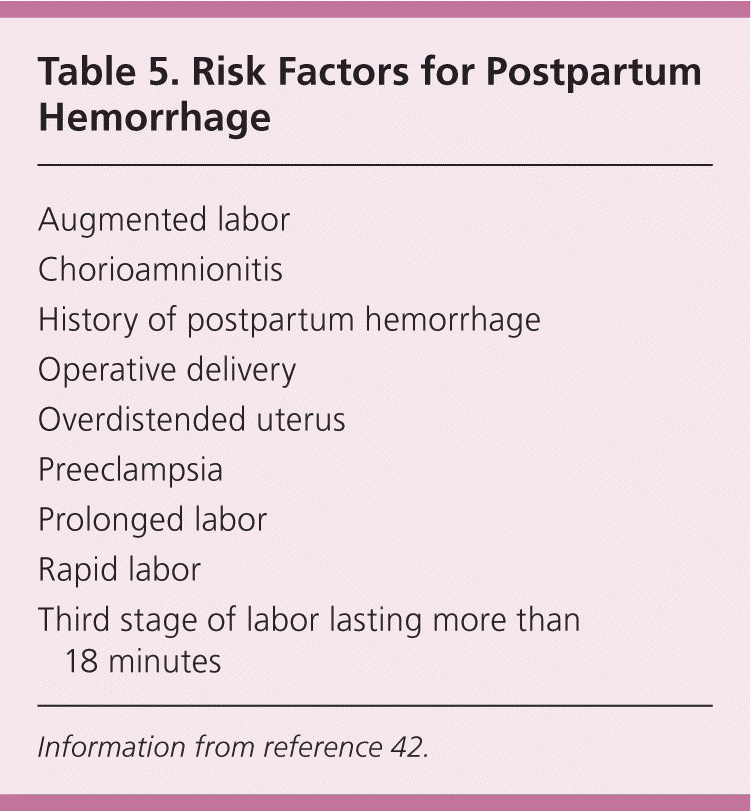
Management of Spontaneous Vaginal Delivery
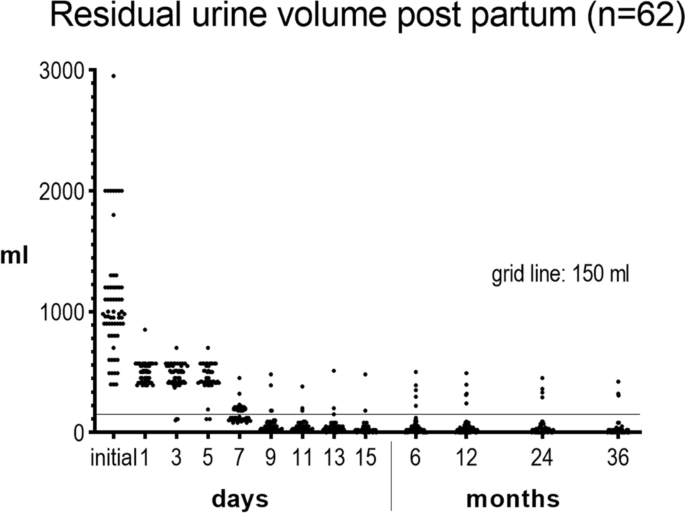
Postpartum urinary retention: what are the sequelae? A long-term

Clinical Practice Guideline on the Management of Urinary Retention

Pregnancy and delivery after mid-urethral sling operation

PDF) Stress urinary incontinence: pre-pregnancy history and

PDF) The risk factors of postpartum urinary retention after