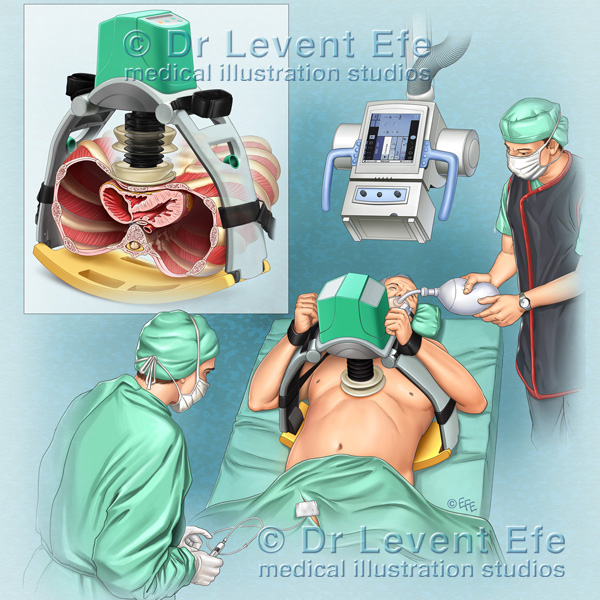
Mechanical vs manual CPR compressions
Meta-analysis of the available research looks at primary and secondary patient outcomes of applying mechanical CPR compression devices following out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Evaluating Effectiveness: Mechanical CPR vs. Manual CPR for Resuscitation in Cardiac Arrest, June 9, 2023, id 131

Safety of mechanical and manual chest compressions in cardiac arrest patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis - ScienceDirect

Bioengineering, Free Full-Text
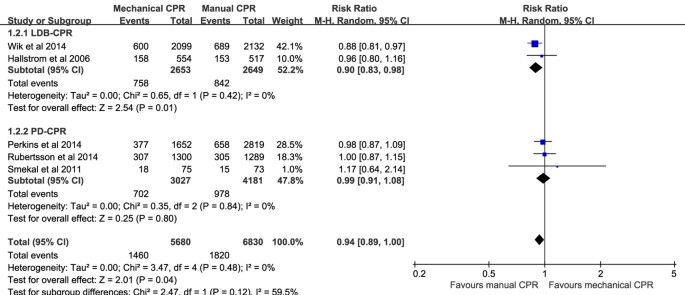
Mechanical versus manual chest compressions for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials

Clinical evidence - LUCAS - Chest Compression System
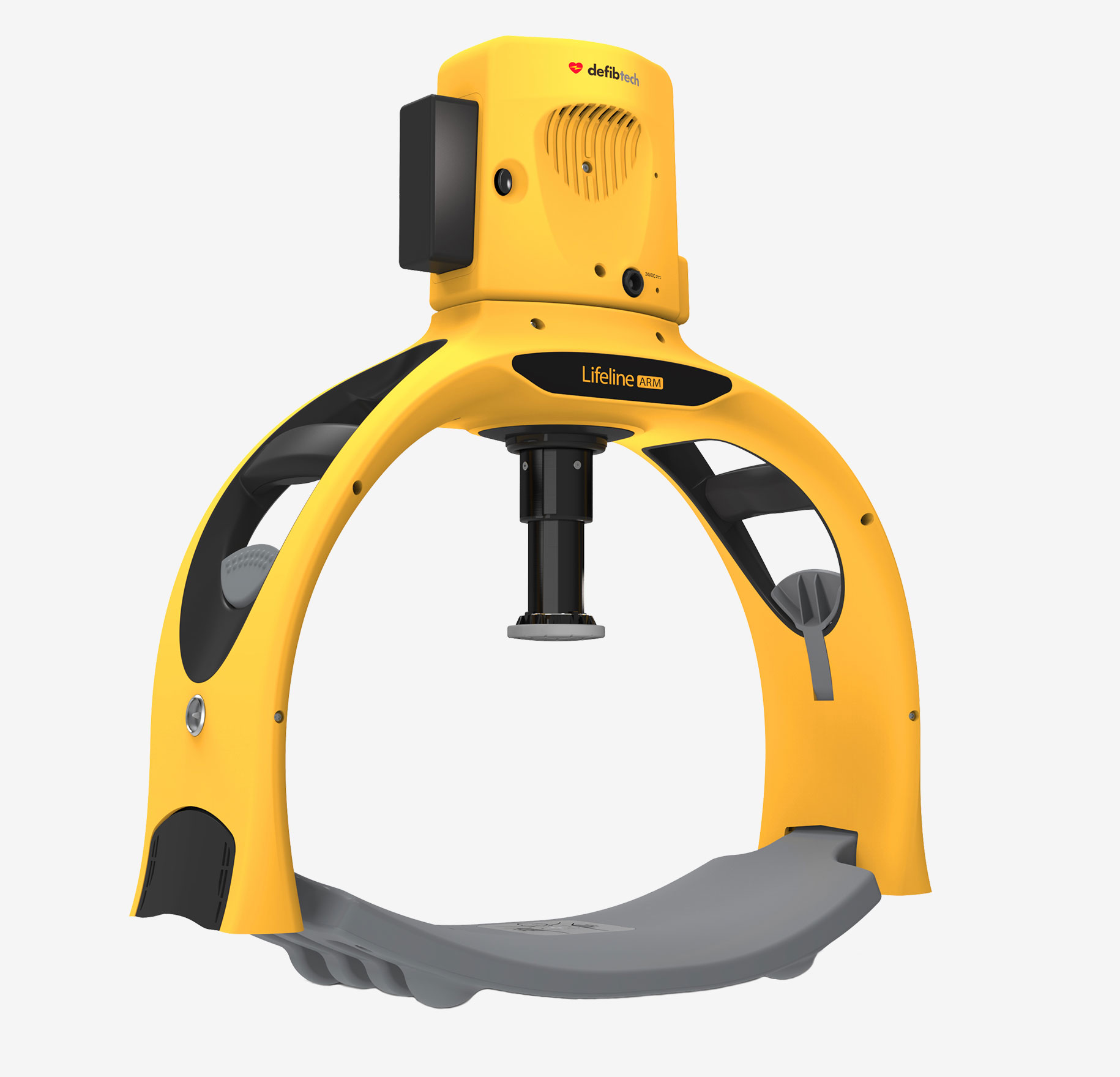

Lifeline Automatic Chest Compressor

Mechanical versus manual chest compression for out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (PARAMEDIC): a pragmatic, cluster randomised controlled trial - The Lancet

Table 1 from Mechanical Chest Compression Devices: Historical Evolution, Classification and Current Practices, A Short Review

Mechanical versus manual chest compressions in the treatment of in-hospital cardiac arrest patients in a non-shockable rhythm: a randomised controlled feasibility trial (COMPRESS-RCT), Scandinavian Journal of Trauma, Resuscitation and Emergency Medicine

LUCAS Versus Manual Chest Compression During Ambulance Transport: A Hemodynamic Study in a Porcine Model of Cardiac Arrest