Hue, Value and Saturation
Hue, Value and Saturation adjustments are demonstrated here with Winsor Lemon, Cadmium Red, Ultramarine (Green Shade) and Titanium White oil paints. Cadmium Red and the Titanium White are mixed to raise the value of the red, which is also referred to as creating a ‘tint’. Then the three primaries are mixed to create a neutral black that is added to the red to reduce saturation and deepen value. Darker values are also called ‘shades’. Black is added to the red to show the shades of red becoming warm, dark values. Then our yellow, Winsor Lemon, is added to red which alters the hue and, as more and more yellow is added, it shifts the red to orange. Then the black mixed earlier is combined with white to come close to the value of Cadmium Red in a mid-tone grey, then it is added in increasing quantity to the red. The result is a desaturated red that retains the same value and a range of warm greys result. It is especially helpful to see the range of dark values that result from these mixtures because there are only chromatic greys in nature and a demonstration like this can help you to achieve them in your work.

Relativity of Color: Hue, Value and Saturation Squares – Cory

Hue, value, and saturation studies!, HVS2a & b

Understanding Color Theory in Game Art Easily - Pixune
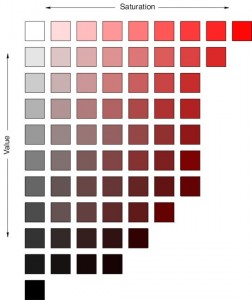
Hue, Value, Saturation

color - How do I calculate average hue, since the numbers loop

Color Relativity

Color Theory for Beginners

What's the difference between color terminology like Hue, Value
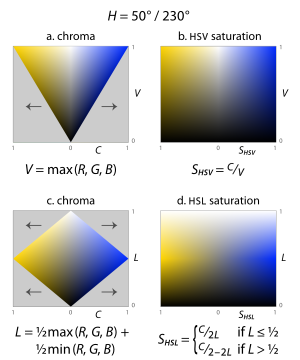
HSL and HSV - Wikipedia
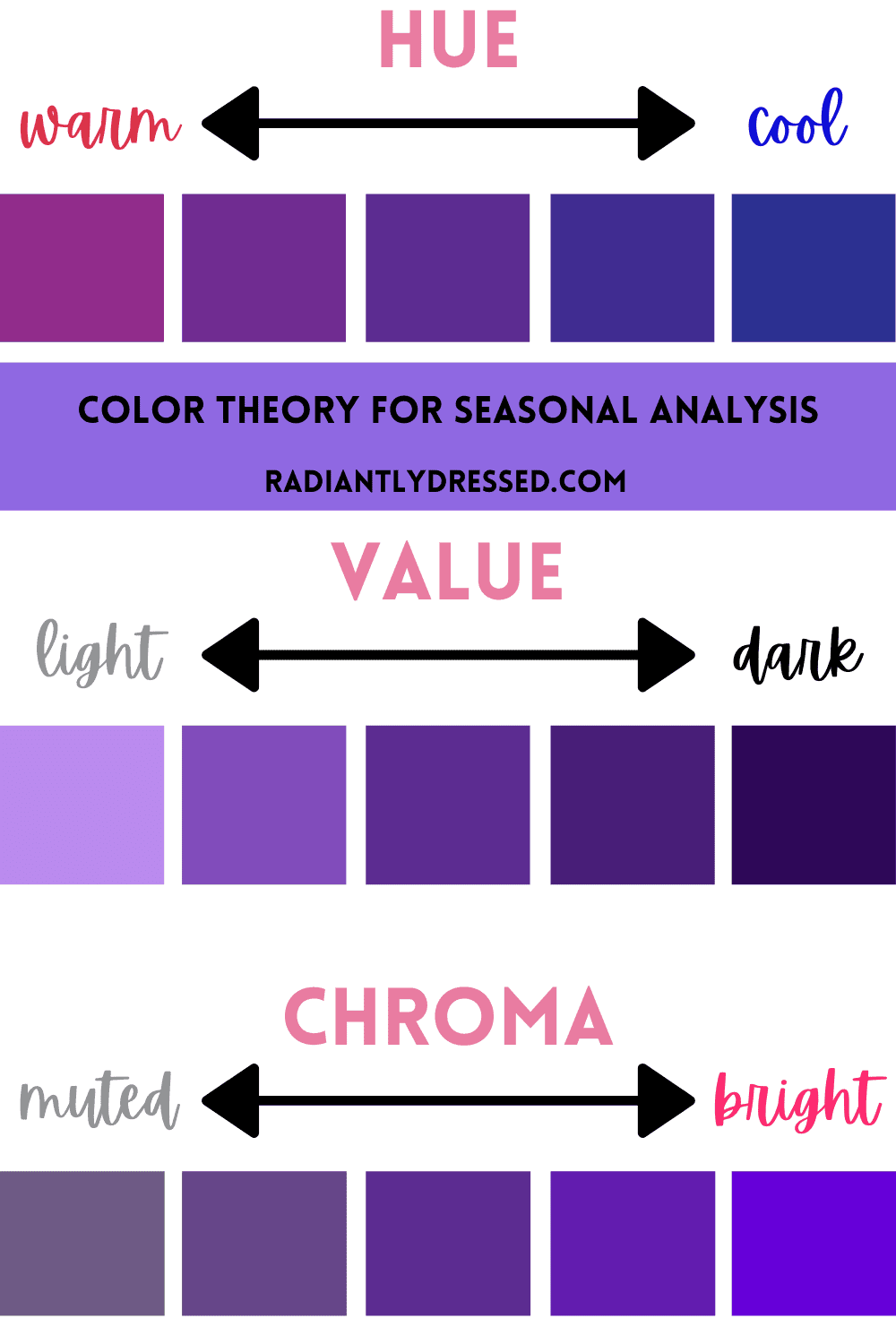
Color Theory for Seasonal Analysis - Radiantly Dressed

The Basics of Color Theory for House Paint - Fine Homebuilding

PPT - Color Harmonies PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID









