Characterization of 46C-NS cells.(A–C) Immunofluorescen

Epsins Regulate Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Exit from Pluripotency and Neural Commitment by Controlling Notch Activation

Epsins Regulate Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Exit from Pluripotency and Neural Commitment by Controlling Notch Activation
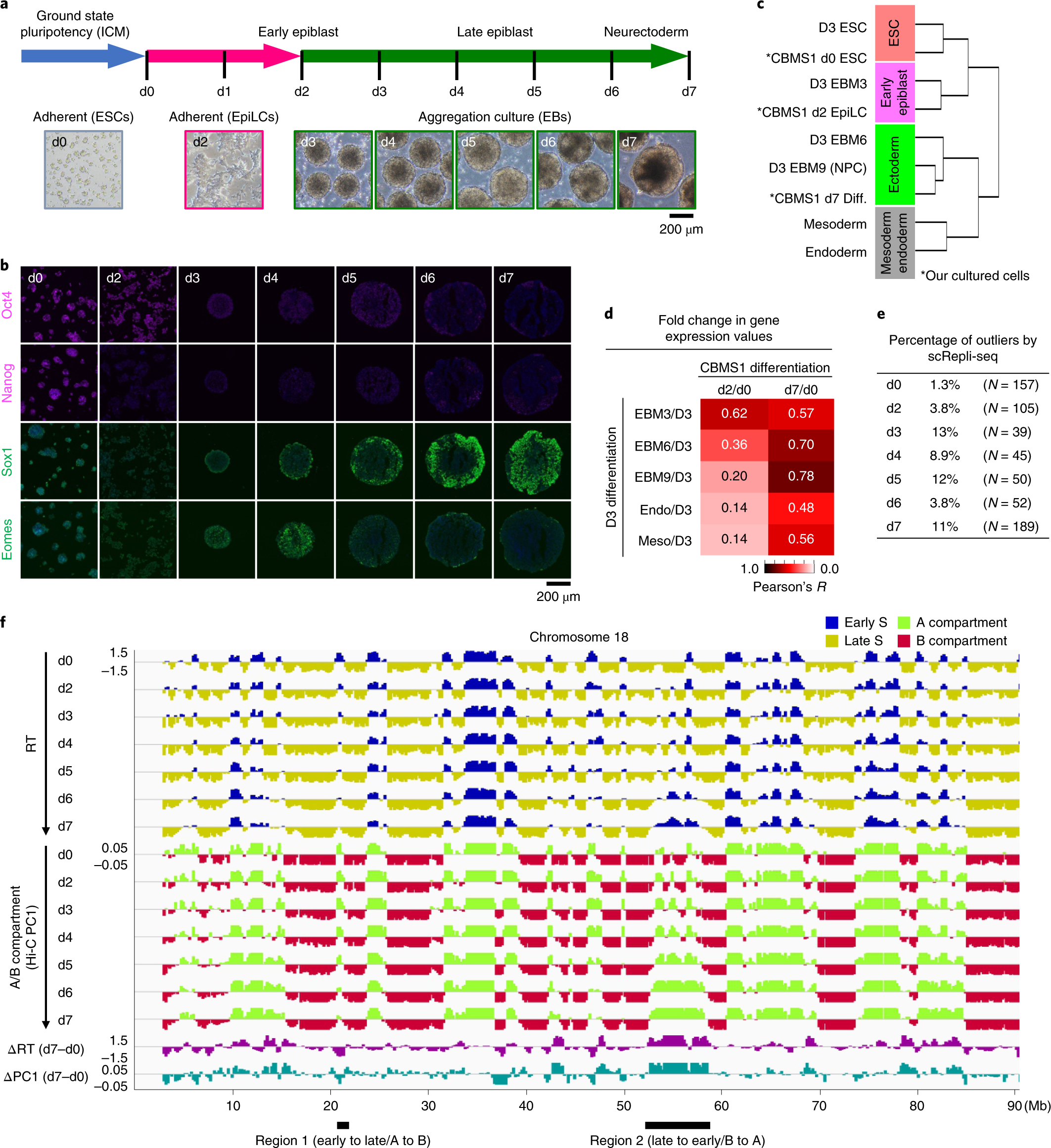
Single-cell DNA replication profiling identifies spatiotemporal developmental dynamics of chromosome organization

NBD-based synthetic probes for sensing small molecules and proteins: design, sensing mechanisms and biological applications. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Reactive X (where X = O, N, S, C, Cl, Br, and I) species nanomedicine - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2CS00435F

Epsins Regulate Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Exit from Pluripotency and Neural Commitment by Controlling Notch Activation

alpha Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody (B-5-1-2) (32-2500)

Phase separation of RNA-binding protein promotes polymerase engagement and transcription

The Apical Polarity Determinant Crumbs 2 Is a Novel Regulator of ESC‐Derived Neural Progenitors - Boroviak - 2011 - STEM CELLS - Wiley Online Library
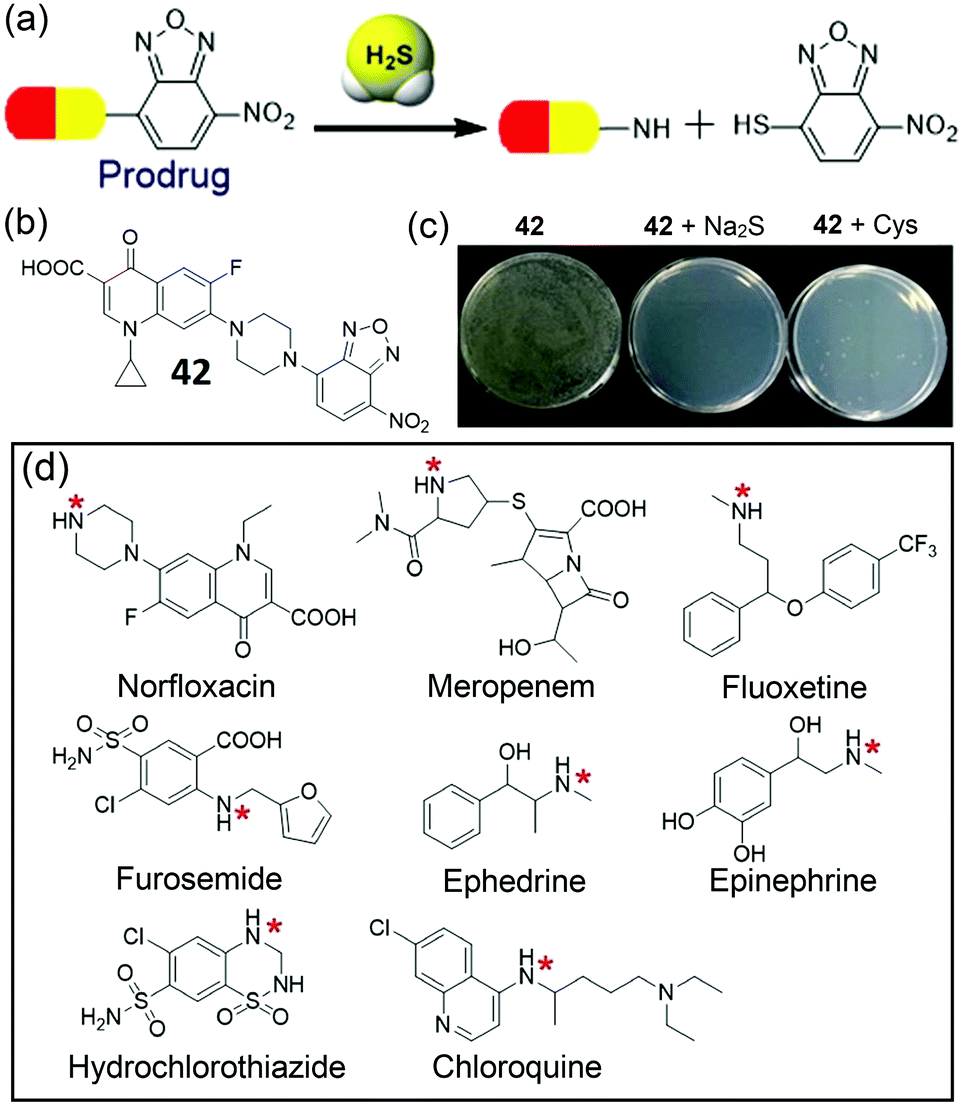
NBD-based synthetic probes for sensing small molecules and proteins: design, sensing mechanisms and biological applications - Chemical Society Reviews (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D0CS01096K

Loss of Dip2b leads to abnormal neural differentiation from mESCs, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

Characterization of 46C-NS cells. (A–C) Immunofluorescence staining

PDF) Detection of anti-nuclear antibodies by indirect immunofluorescence on HEp-2 cells: setting the appropriate screening dilution for the diagnosis of autoimmune rheumatic diseases

Forced expression of the motor neuron determinant HB9 in neural stem cells affects neurogenesis - ScienceDirect









